Program Target FPGA Boards or SoC Devices
To configure or program the connected target SoC device or FPGA board, use the
IP Core Generation workflow in the HDL Workflow Advisor.
How to Program Target Device
Using the Workflow Advisor UI
Open the HDL Workflow Advisor. Right-click the DUT Subsystem that contains the algorithm to be deployed on the target FPGA, and select HDL Code > HDL Workflow Advisor.
In the Set Target Device and Synthesis Tool task, specify
IP Core Generationas the Target workflow, and specify a Target platform other than theGeneric Xilinx PlatformorGeneric Altera Platform.Right-click the Program Target Device task and select Run to Selected Task.
In the Program Target Device task, specify the Programming method, and run this task.
To learn more about the HDL Workflow Advisor, see Getting Started with the HDL Workflow Advisor.
Using the Workflow Advisor Script
To program the target device at the command line, after you specify the target
workflow and target platform in the Set Target Device and Synthesis
Tool task, export the HDL Workflow Advisor settings to a script.
In the HDL Workflow Advisor window, select File > Export to Script. The script creates and configures an
hdlcoder.WorkflowConfig object that is denoted by
hWC.
Before you run the script, you can specify how to program the target hardware
by using the ProgrammingMethod property of the
WorkflowConfig object.This code snippet shows an example
script that is exported from the HDL Workflow Advisor when you use the default
Download
Programming method. To run the Program Target
Device task, customize this script by setting the
RunTaskProgramTargetDevice attribute of the
WorkflowConfig object to true.
% This script was generated using the following parameter values: % ... % Set properties related to 'RunTaskProgramTargetDevice' Task hWC.RunTaskProgramTargetDevice = true; hWC.ProgrammingMethod = hdlcoder.ProgrammingMethod.Download; % Validate the Workflow Configuration Object hWC.validate; %% Run the workflow hdlcoder.runWorkflow('hdlcoder_led_blinking/led_counter', hWC);
After you run the Build FPGA Bitstream task, the Workflow Advisor provides you a link to generate a Workflow script that programs the target device without rerunning the previous tasks in the Workflow Advisor.
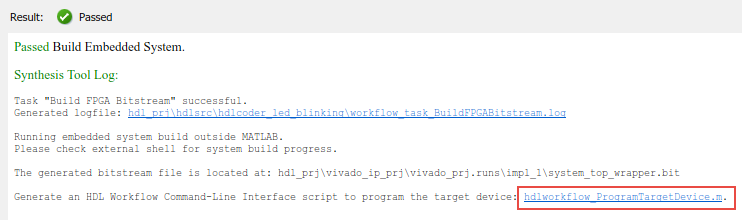
Click the link to open the script in the MATLAB® Editor. This code snippet shows an example script that is generated by the HDL Workflow Advisor. If close the HDL Workflow Advisor, you can run the script to program the target hardware without running other workflow tasks.
% Load the Model % ... % Set Workflow tasks to run hWC.RunTaskGenerateRTLCodeAndIPCore = false; hWC.RunTaskCreateProject = false; hWC.RunTaskGenerateSoftwareInterface = false; hWC.RunTaskBuildFPGABitstream = false; hWC.RunTaskProgramTargetDevice = true; % Set properties related to 'RunTaskProgramTargetDevice' Task hWC.ProgrammingMethod = hdlcoder.ProgrammingMethod.Download; % Validate the Workflow Configuration Object hWC.validate;
Programming Methods
Download
If you use the reference designs for Xilinx®
Zynq® and Intel® SoC hardware platforms, the code generator uses
Download as the default Programming
method.
When you use Download as the Programming
method and run the Program Target Device
task, HDL Coder™ copies the generated FPGA bitstream, Linux devicetree, and system
initialization scripts to the SD card on the target board, and then keeps the
bitstream on the SD card persistently. To use this programming method, you do
not require an Embedded Coder® license. You can create an SSH object by specifying the
IP Address, SSH Username, and
SSH Password. HDL Coder uses the SSH object to copy the bitstream to the SD card and
reprogram the board.
It is recommended that you use the Download method, because
this method programs the FPGA bitstream and loads the corresponding Linux
devicetree before booting the Linux system. Therefore, the
Download method is more robust and does not result in a
kernel panic or kernel hang on boot up. During the Linux reboot, the FPGA
bitstream is reprogrammed from the SD card automatically. To specify
Download as the Programming method
when you run the workflow using the Workflow Advisor script, before you run the
script, make sure that the ProgrammingMethod property of
the WorkflowConfig object, hWC, is set to
Download.
hWC.ProgrammingMethod = hdlcoder.ProgrammingMethod.Download;
JTAG
When you specify JTAG as the Programming
method and run the Program Target Device
task, HDL Coder uses a JTAG cable to program the target SoC device. Use this
method to program Intel and Xilinx SoC devices and standalone FPGA boards.
For programming SoC devices, it is recommended that you use the
Download method. The JTAG mode does
not involve the ARM processor and programs the onboard FPGA directly. This mode
does not update the Linux devicetree, and can crash the Linux system or result
in a kernel panic when the bitstream does not match the devicetree. To avoid
this situation, use the Download method to program the SoC
device.
The standalone Intel and Xilinx FPGA boards do not have an embedded ARM processor.
JTAG is the default method that you use to program the
FPGA boards.
To specify JTAG as the Programming
method when you run the workflow using the Workflow Advisor
script, before you run the script, change the
ProgrammingMethod property of the WorkflowConfig
object, hWC, to
JTAG.
hWC.ProgrammingMethod = hdlcoder.ProgrammingMethod.JTAG;
Custom
To program the target device, you can specify a custom programming method when
you create your own custom reference design. Use the
CallbackCustomProgrammingMethod of the
hdlcoder.ReferenceDesign class to register a function handle
for the callback function that gets executed when running the Program
Target Device task. To define your callback function, create a
file that defines a MATLAB function and add the file to your MATLAB path.
This example code snippet shows a reference design definition file that uses a
custom programming method. To learn more, see CallbackCustomProgrammingMethod.
unction hRD = plugin_rd() % Reference design definition % ... % Construct reference design object hRD = hdlcoder.ReferenceDesign('SynthesisTool', 'Xilinx Vivado'); hRD.ReferenceDesignName = 'Parameter Callback Custom'; hRD.BoardName = 'ZedBoard'; % Tool information hRD.SupportedToolVersion = {'2017.2'}; % ... hRD.CallbackCustomProgrammingMethod = @my_reference_design.callback_CustomProgrammingMethod;
Related Examples
- Define Custom Board and Reference Design for Zynq Workflow
- Define Custom Board and Reference Design for Intel SoC Workflow