CAN Unpack
Unpack individual signals from CAN messages
Library
Vehicle Network Toolbox™ > CAN Communication
Embedded Coder® > Embedded Targets > Host Communication
Description
The CAN Unpack block unpacks a CAN message into signal data using the specified output parameters at every time step. Data is output as individual signals.
To use this block, you also need a license for Simulink® software.
The CAN Unpack block has one output port by default. The number of output ports is dynamic and depends on the number of signals that you specify for the block to output. For example, if your block has four signals, the block has four output ports.
The CAN Unpack block supports:
The use of Simulink Accelerator™ Rapid Accelerator mode. Using this feature, you can speed up the execution of Simulink models.
The use of model referencing. Using this feature, your model can include other Simulink models as modular components.
Code generation to deploy models to targets. Code generation is not supported if your signal information consists of signed or unsigned integers greater than 32 bits long.
For more information on these features, see Design Your Model for Effective Acceleration.
Dialog Box
To select your CAN message unpacking parameters, use the Function Block Parameters dialog box .
Parameters
- Data to be output as
Select your data signal:
raw data: Output data as a uint8 vector array. If you select this option, you specify only the message fields. The other signal parameter fields are unavailable. This option opens only one output port on your block.
manually specified signals: You can specify data signals. If you select this option, use the
Signalstable to create your signals message manually. The number of output ports on your block depends on the number of signals that you specify. For example, if you specify four signals, your block has four output ports.CANdb specified signals: You can specify a CAN database file that contains data signals. If you select this option, select a CANdb file. The number of output ports on your block depends on the number of signals specified in the CANdb file. For example, if the selected message in the CANdb file has four signals, your block has four output ports.
For manually or CANdb specified signals, the default output signal data type is double. To specify other types, use a Signal Specification block. This allows the block to support the following output signal data types: single, double, int8, int16, int32, int64, uint8, uint16, uint32, uint64, and boolean. The block does not support fixed-point types.
- CANdb file
This option is available if you specify that your data is input via a CANdb file in the Data to be output as list. Click Browse to find the CANdb file on your system. The messages and signal definitions specified in the CANdb file populate the Message section of the dialog box. The signals specified in the CANdb file populate Signals table.
File names that contain non-alphanumeric characters such as equal signs, ampersands, and so forth are not valid CAN database file names. You can use periods in your database name. Rename CAN database files with non-alphanumeric characters before you use them.
- Message list
This option is available if you specify in the Data to be output as list that your data is to be output as a CANdb file and you select a CANdb file in the CANdb file field. You can select the message that you want to view. The Signals table then displays the details of the selected message.
Message
- Name
Specify a name for your CAN message. The default is
CAN Msg. This option is available if you choose to output raw data or manually specify signals.- Identifier type
Specify whether your CAN message identifier is a
Standardor anExtendedtype. The default isStandard. A standard identifier is an 11-bit identifier and an extended identifier is a 29-bit identifier. This option is available if you choose to output raw data or manually specify signals. For CANdb-specified signals, the Identifier type inherits the type from the database.- Identifier
Specify your CAN message ID. This number must be a integer from 0 through 2047 for a standard identifier and from 0 through 536870911 for an extended identifier. If you specify
-1, the block unpacks the messages that match the length specified for the message. You can also specify hexadecimal values by using thehex2decfunction. This option is available if you choose to output raw data or manually specify signals.- Length (bytes)
Specify the length of your CAN message from 0 to 8 bytes. If you are using
CANdb specified signalsfor your output data, the CANdb file defines the length of your message. If not, this field defaults to8. This option is available if you choose to output raw data or manually specify signals.
Signals Table
If you choose to specify signals manually or define signals by using a CANdb file, this table appears.
If you are using a CANdb file, the data in the file populates this table and you cannot edit the fields. To edit signal information, switch to specified signals.
If you have selected to specify signals manually, create your signals manually in this table. Each signal that you create has these values:
- Name
Specify a descriptive name for your signal. The Simulink block in your model displays this name. The default is
Signal [row number].- Start bit
Specify the start bit of the data. The start bit is the least significant bit counted from the start of the message. The start bit must be an integer from 0 through 63.
- Length (bits)
Specify the number of bits the signal occupies in the message. The length must be an integer from 1 through 64.
- Byte order
Select either of these options:
LE: Where the byte order is in little-endian format (Intel®). In this format you count bits from the least-significant bit to the most-significant bit. For example, if you pack one byte of data in little-endian format, with the start bit at 20, the data bit table resembles this figure.Little-Endian Byte Order Counted from the Least Significant Bit to the Highest Address
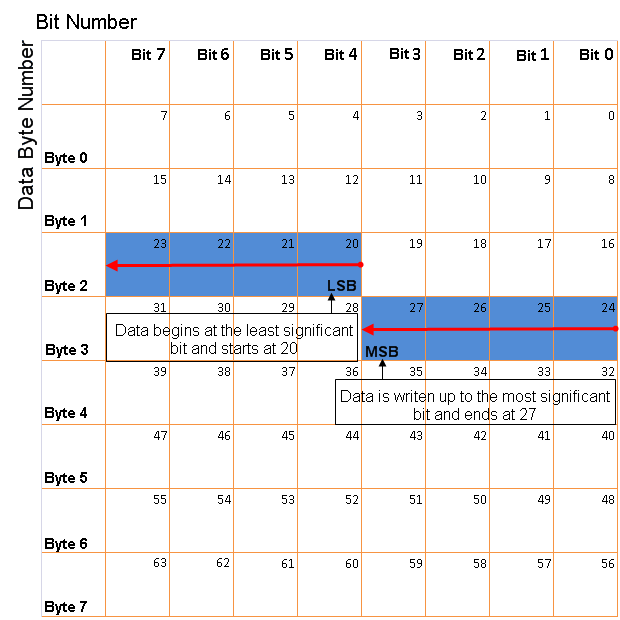
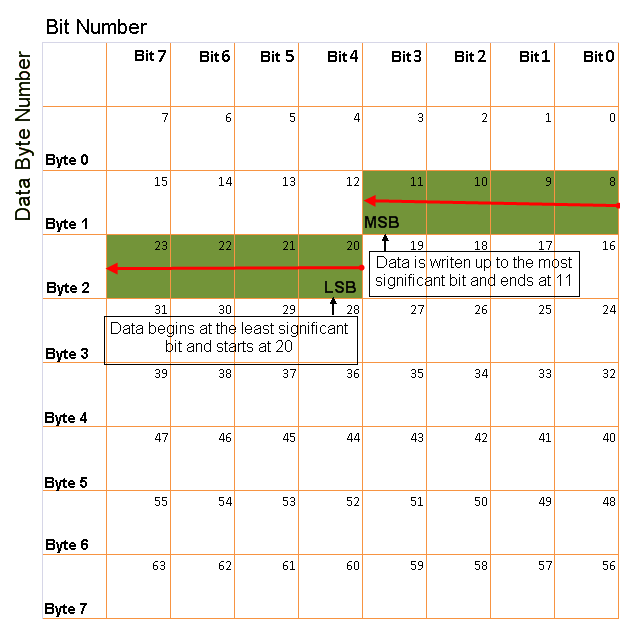
BE: Where the byte order is in big-endian format (Motorola®). In this format you count bits from the least-significant bit to the most-significant bit. For example, if you pack one byte of data in big-endian format, with the start bit at 20, the data bit table resembles this figure.Big-Endian Byte Order Counted from the Least Significant Bit to the Lowest Address
- Data type
Specify how the signal interprets the data in the allocated bits. Choose from:
signed(default)unsignedsingledouble
- Multiplex type
Specify how the block unpacks the signals from the CAN message at each time step:
Standard: The signal is unpacked at each time step.Multiplexor: TheMultiplexorsignal or the mode signal is unpacked. You can specify only oneMultiplexorsignal per message.Multiplexed: The signal is unpacked if the value of theMultiplexorsignal (mode signal) at run time matches the configured Multiplex value of this signal.
For example, a message has four signals with these values.
Signal Name Multiplex Type Multiplex Value Signal-A Standard Not applicable Signal-B Multiplexed 1 Signal-C Multiplexed 0 Signal-D Multiplexor Not applicable In this example:
The block unpacks Signal-A (Standard signal) and Signal-D (Multiplexor signal) in every time step.
If the value of Signal-D is 1 at a particular time step, then the block unpacks Signal-B along with Signal-A and Signal-D in that time step.
If the value of Signal-D is 0 at a particular time step, then the block unpacks Signal-C along with Signal-A and Signal-D in that time step.
If the value of Signal-D is not 1 or 0, the block does not unpack either of the Multiplexed signals in that time step.
- Multiplex value
This option is available only if you have selected the Multiplex type to be
Multiplexed. The value you provide must match theMultiplexorsignal value at run time for the block to unpack theMultiplexedsignal. The Multiplex value must be a positive integer or zero.- Factor
Specify the Factor value applied to convert the unpacked raw value to the physical value (signal value). For more information, see Conversion Formula.
- Offset
Specify the Offset value applied to convert the physical value (signal value) to the unpacked raw value. For more information, see Conversion Formula.
- Min, Max
Define a range of raw signal values. The default settings are
-Inf(negative infinity) andInf, respectively. For CANdb specified signals, these settings are read from the CAN database. For manually specified signals, you can specify the minimum and maximum physical value of the signal. By default, these settings do not clip signal values that exceed them.
Output Ports
Selecting an Output ports option adds an output port to your block.
- Output identifier
Select this option to output a CAN message identifier. The data type of this port is uint32.
- Output remote
Select this option to output the message remote frame status. This option adds a new output port to the block. The data type of this port is uint8.
- Output timestamp
Select this option to output the message timestamp. This value indicates when the message was received, measured as the number of seconds elapsed since the model simulation began. This option adds a new output port to the block. The data type of this port is double.
- Output length
Select this option to output the length of the message in bytes. This option adds a new output port to the block. The data type of this port is uint8.
- Output error
Select this option to output the message error status. This option adds a new output port to the block. An output value of
1on this port indicates that the incoming message is an error frame. If the output value is0, there is no error. The data type of this port is uint8.- Output status
Select this option to output the message received status. The status is
1if the block receives a new message and0if it does not. This option adds a new output port to the block. The data type of this port is uint8.
If you do not select an Output ports option, the number of output ports on your block depends on the number of signals that you specify.
Conversion Formula
The conversion formula is:
physical_value = raw_value * Factor + Offset
raw_value is the unpacked signal value and
physical_value is the scaled signal value.