wpdec2
Wavelet packet decomposition 2-D
Syntax
T = wpdec2(X,N,wname,E,P)
T = wpdec2(X,N,wname)
T = wpdec2(X,N,wname,'shannon')
Description
wpdec2 is a two-dimensional
wavelet packet analysis function.
T = wpdec2(X,N, returns a wavelet packet
tree wname,E,P)T corresponding to the wavelet packet decomposition of the
matrix X, at level N, with the specified wavelet
wname (see wfilters for more information).
T = wpdec2(X,N, is equivalent to
wname)T = wpdec2(X,N,.wname,'shannon')
E is a character vector or string scalar containing the type of entropy and
P is an optional parameter depending on the value of
T (see wentropy for more information).
| Entropy Type Name (E) | Parameter (P) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
'shannon' | P is not used. | |
'log energy' | P is not used. | |
'threshold' | 0 ≤ P | P is the threshold. |
'sure' | 0 ≤ P | P is the threshold. |
'norm' | 1 ≤ P | P is the power. |
'user' | Character vector or string scalar | P is a character vector or string scalar
containing the file name of your own entropy function, with a single
input X. |
FunName | No constraints on P |
|
Note
The 'user' option is historical and still
kept for compatibility, but it is obsoleted by the last option described
in the preceding table. The FunName option does
the same as the 'user' option and in addition,
allows you to pass a parameter to your own entropy function.
See wpdec for a more
complete description of the wavelet packet decomposition.
Examples
% The current extension mode is zero-padding (see dwtmode).
% Load image.
load tire
% X contains the loaded image.
% For an image the decomposition is performed using:
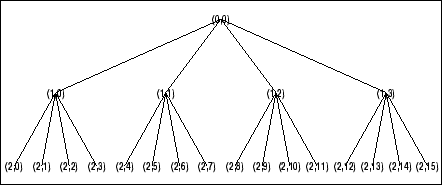
t = wpdec2(X,2,'db1');
% The default entropy is shannon.
% Plot wavelet packet tree
% (quarternary tree, or tree of order 4).
plot(t)
Tips
When X represents an indexed image, X is an m-by-n matrix.
When X represents a truecolor image, it is an m-by-n-by-3
array, where each m-by-n matrix
represents a red, green, or blue color plane concatenated along the
third dimension.
For more information on image formats, see the image and imfinfo reference
pages.
Algorithms
The algorithm used for the wavelet packets decomposition follows
the same line as the wavelet decomposition process (see dwt2 and wavedec2 for
more information).
References
Coifman, R.R.; M.V. Wickerhauser (1992), “Entropy-based algorithms for best basis selection,” IEEE Trans. on Inf. Theory, vol. 38, 2, pp. 713–718.
Meyer, Y. (1993), Les ondelettes. Algorithmes et applications, Colin Ed., Paris, 2nd edition. (English translation: Wavelets: Algorithms and Applications, SIAM).
Wickerhauser, M.V. (1991), “INRIA lectures on wavelet packet algorithms,” Proceedings ondelettes et paquets d'ondes, 17–21 June, Rocquencourt, France, pp. 31–99.
Wickerhauser, M.V. (1994), Adapted wavelet analysis from theory to software Algorithms, A.K. Peters.