ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer
Coder configurer for linear binary classification of high-dimensional data
Description
A ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer object is a coder
configurer of a linear classification model (ClassificationLinear) used for binary classification of high-dimensional
data.
A coder configurer offers convenient features to configure code generation options, generate C/C++ code, and update model parameters in the generated code.
Configure code generation options and specify the coder attributes of linear model parameters by using object properties.
Generate C/C++ code for the
predictandupdatefunctions of the linear classification model by usinggenerateCode. Generating C/C++ code requires MATLAB® Coder™.Update model parameters in the generated C/C++ code without having to regenerate the code. This feature reduces the effort required to regenerate, redeploy, and reverify C/C++ code when you retrain the linear model with new data or settings. Before updating model parameters, use
validatedUpdateInputsto validate and extract the model parameters to update.
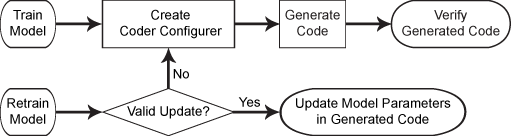
This flow chart shows the code generation workflow using a coder configurer.
For the code generation usage notes and limitations of a linear classification model, see
the Code Generation sections of ClassificationLinear, predict, and update.
Creation
After training a linear classification model by using fitclinear, create a coder configurer for the model by using learnerCoderConfigurer. Use the properties of a coder configurer to specify the
coder attributes of the predict and update arguments.
Then, use generateCode to generate C/C++ code based on the specified
coder attributes.
Properties
predict Arguments
The properties listed in this section specify the coder attributes of the predict function arguments in the generated code.
X — Coder attributes of predictor data
LearnerCoderInput object
Coder attributes of the predictor data to pass to the generated C/C++ code for the
predict function of the linear
classification model, specified as a LearnerCoderInput object.
When you create a coder configurer by using the learnerCoderConfigurer function, the input argument X determines the default values of the LearnerCoderInput coder attributes:
SizeVector— The default value is the array size of the inputX.If the
Valueattribute of theObservationsInproperty for theClassificationLinearCoderConfigureris'rows', then thisSizeVectorvalue is[n p], wherencorresponds to the number of observations andpcorresponds to the number of predictors.If the
Valueattribute of theObservationsInproperty for theClassificationLinearCoderConfigureris'columns', then thisSizeVectorvalue is[p n].
To switch the elements of
SizeVector(for example, to change[n p]to[p n]), modify theValueattribute of theObservationsInproperty for theClassificationLinearCoderConfigureraccordingly. You cannot modify theSizeVectorvalue directly.VariableDimensions— The default value is[0 0], which indicates that the array size is fixed as specified inSizeVector.You can set this value to
[1 0]if theSizeVectorvalue is[n p]or to[0 1]if it is[p n], which indicates that the array has variable-size rows and fixed-size columns. For example,[1 0]specifies that the first value ofSizeVector(n) is the upper bound for the number of rows, and the second value ofSizeVector(p) is the number of columns.DataType— This value issingleordouble. The default data type depends on the data type of the inputX.Tunability— This value must betrue, meaning thatpredictin the generated C/C++ code always includes predictor data as an input.
You can modify the coder attributes by using dot notation. For example, to generate C/C++ code
that accepts predictor data with 100 observations (in rows) of three predictor variables (in
columns), specify these coder attributes of X for the coder configurer
configurer:
configurer.X.SizeVector = [100 3];
configurer.X.DataType = 'double';
configurer.X.VariableDimensions = [0 0];[0
0] indicates that the first and second dimensions of X
(number of observations and number of predictor variables, respectively) have fixed
sizes.To allow the generated C/C++ code to accept predictor data with up to 100 observations,
specify these coder attributes of
X:
configurer.X.SizeVector = [100 3];
configurer.X.DataType = 'double';
configurer.X.VariableDimensions = [1 0];[1
0] indicates that the first dimension of X (number of
observations) has a variable size and the second dimension of X (number
of predictor variables) has a fixed size. The specified number of observations, 100 in this
example, becomes the maximum allowed number of observations in the generated C/C++ code. To
allow any number of observations, specify the bound as Inf.
ObservationsIn — Coder attributes of predictor data observation dimension
EnumeratedInput object
Coder attributes of the predictor data observation dimension ('ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument of predict), specified as an EnumeratedInput object.
When you create a coder configurer by using the learnerCoderConfigurer function, the 'ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument determines the default values of the EnumeratedInput coder attributes:
Value— The default value is the predictor data observation dimension you use when creating the coder configurer, specified as'rows'or'columns'. If you do not specify'ObservationsIn'when creating the coder configurer, the default value is'rows'.SelectedOption— This value is always'Built-in'. This attribute is read-only.BuiltInOptions— Cell array of'rows'and'columns'. This attribute is read-only.IsConstant— This value must betrue.Tunability— The default value isfalseif you specify'ObservationsIn','rows'when creating the coder configurer, andtrueif you specify'ObservationsIn','columns'. If you setTunabilitytofalse, the software setsValueto'rows'. If you specify other attribute values whenTunabilityisfalse, the software setsTunabilitytotrue.
NumOutputs — Number of outputs in predict
1 (default) | 2
Number of output arguments to return from the generated C/C++ code for the
predict function of the linear
classification model, specified as 1 or 2.
The output arguments of predict are Label (predicted class labels) and Score (classification scores), in that order. predict
in the generated C/C++ code returns the first n outputs of the
predict function, where
n is the NumOutputs value.
After creating the coder configurer configurer, you can
specify the number of outputs by using dot
notation.
configurer.NumOutputs = 2;
The NumOutputs property is equivalent to the
'-nargout' compiler option of codegen (MATLAB Coder). This option specifies the number of output arguments in the
entry-point function of code generation. The object function generateCode generates two entry-point
functions—predict.m and update.m for the
predict and update
functions of a linear classification model, respectively—and generates C/C++ code for
the two entry-point functions. The specified value for the
NumOutputs property corresponds to the number of output
arguments in the entry-point function predict.m.
Data Types: double
update Arguments
The properties listed in this section specify the coder
attributes of the update function
arguments in the generated code. The update function takes a trained model
and new model parameters as input arguments, and returns an updated version of the model that
contains the new parameters. To enable updating the parameters in the generated code, you need
to specify the coder attributes of the parameters before generating code. Use a LearnerCoderInput
object to specify the coder attributes of each parameter. The default attribute values are based
on the model parameters in the input argument Mdl of learnerCoderConfigurer.
Beta — Coder attributes of linear predictor coefficients
LearnerCoderInput object
Coder attributes of the linear predictor coefficients (Beta of a linear classification
model), specified as a LearnerCoderInput object.
The default attribute values of the
LearnerCoderInput object are based on the input argument
Mdl of learnerCoderConfigurer:
SizeVector— This value must be[p 1], wherepis the number of predictors inMdl.VariableDimensions— This value must be[0 0], indicating that the array size is fixed as specified inSizeVector.DataType— This value is'single'or'double'. The default data type is consistent with the data type of the training data you use to trainMdl.Tunability— This value must betrue.
Bias — Coder attributes of bias term
LearnerCoderInput object
Coder attributes of the bias term (Bias of a linear classification
model), specified as a LearnerCoderInput object.
The default attribute values of the
LearnerCoderInput object are based on the input argument
Mdl of learnerCoderConfigurer:
SizeVector— This value must be[1 1].VariableDimensions— This value must be[0 0], indicating that the array size is fixed as specified inSizeVector.DataType— This value is'single'or'double'. The default data type is consistent with the data type of the training data you use to trainMdl.Tunability— This value must betrue.
Cost — Coder attributes of misclassification cost
LearnerCoderInput object
Coder attributes of the misclassification cost (Cost of a linear classification
model), specified as a LearnerCoderInput object.
The default attribute values of the
LearnerCoderInput object are based on the input argument
Mdl of learnerCoderConfigurer:
SizeVector— This value must be[2 2].VariableDimensions— This value must be[0 0], indicating that the array size is fixed as specified inSizeVector.DataType— This value is'single'or'double'. The default data type is consistent with the data type of the training data you use to trainMdl.Tunability— The default value istrue.
Prior — Coder attributes of prior probabilities
LearnerCoderInput object
Coder attributes of the prior probabilities (Prior of a linear
classification model), specified as a LearnerCoderInput object.
The default attribute values of the
LearnerCoderInput object are based on the input argument
Mdl of learnerCoderConfigurer:
SizeVector— This value must be[1 2].VariableDimensions— This value must be[0 0], indicating that the array size is fixed as specified inSizeVector.DataType— This value is'single'or'double'. The default data type is consistent with the data type of the training data you use to trainMdl.Tunability— The default value istrue.
Other Configurer Options
OutputFileName — File name of generated C/C++ code
'ClassificationLinearModel' (default) | character vector
File name of the generated C/C++ code, specified as a character vector.
The object function generateCode of
ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer generates C/C++ code using this file name.
The file name must not contain spaces because they can lead to code generation failures in certain operating system configurations. Also, the name must be a valid MATLAB function name.
After creating the coder configurer configurer, you can specify the file
name by using dot
notation.
configurer.OutputFileName = 'myModel';Data Types: char
Verbose — Verbosity level
true (logical 1) (default) | false (logical 0)
Verbosity level, specified as true (logical 1) or
false (logical 0). The verbosity level controls the display of
notification messages at the command line.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
true (logical 1) | The software displays notification messages when your changes to the coder attributes of a parameter result in changes for other dependent parameters. |
false (logical
0) | The software does not display notification messages. |
To enable updating machine learning model parameters in the generated code, you need to configure the coder attributes of the parameters before generating code. The coder attributes of parameters are dependent on each other, so the software stores the dependencies as configuration constraints. If you modify the coder attributes of a parameter by using a coder configurer, and the modification requires subsequent changes to other dependent parameters to satisfy configuration constraints, then the software changes the coder attributes of the dependent parameters. The verbosity level determines whether or not the software displays notification messages for these subsequent changes.
After creating the coder configurer configurer, you can modify the
verbosity level by using dot
notation.
configurer.Verbose = false;
Data Types: logical
Options for Code Generation Customization
To customize the code generation workflow, use the generateFiles function and the following three properties with codegen (MATLAB Coder), instead of using the generateCode function.
After generating the two entry-point function files (predict.m and
update.m) by using the generateFiles
function, you can modify these files according to your code generation workflow. For
example, you can modify the predict.m file to include data preprocessing,
or you can add these entry-point functions to another code generation project. Then, you can
generate C/C++ code by using the codegen (MATLAB Coder) function and the
codegen arguments appropriate for the modified entry-point
functions or code generation project. Use the three properties described in this section as
a starting point to set the codegen arguments.
CodeGenerationArguments — codegen arguments
cell array
This property is read-only.
codegen (MATLAB Coder) arguments, specified as a cell array.
This property enables you to customize the code generation workflow. Use the generateCode function if you do not need to customize your
workflow.
Instead of using generateCode with the coder configurer configurer,
you can generate C/C++ code as
follows:
generateFiles(configurer)
cgArgs = configurer.CodeGenerationArguments;
codegen(cgArgs{:})cgArgs accordingly
before calling codegen.
If you modify other properties of configurer, the software updates
the CodeGenerationArguments property accordingly.
Data Types: cell
PredictInputs — List of tunable input arguments of predict
cell array
This property is read-only.
List of tunable input arguments of the entry-point function
predict.m for code generation, specified as a cell array. The
cell array contains another cell array that includes coder.PrimitiveType (MATLAB Coder) objects and coder.Constant (MATLAB Coder) objects.
If you modify the coder attributes of predict arguments,
then the software updates the corresponding objects accordingly. If you specify the
Tunability attribute as false, then the
software removes the corresponding objects from the PredictInputs
list.
The cell array in PredictInputs is equivalent to
configurer.CodeGenerationArguments{6} for the coder configurer
configurer.
Data Types: cell
UpdateInputs — List of tunable input arguments of update
cell array of a structure including coder.PrimitiveType objects
This property is read-only.
List of the tunable input arguments of the entry-point function update.m
for code generation, specified as a cell array of a structure including coder.PrimitiveType (MATLAB Coder) objects. Each coder.PrimitiveType
object includes the coder attributes of a tunable machine learning model
parameter.
If you modify the coder attributes of a model parameter by using the coder configurer
properties (update Arguments properties), then the software
updates the corresponding coder.PrimitiveType object accordingly. If
you specify the Tunability attribute of a machine learning model
parameter as false, then the software removes the corresponding
coder.PrimitiveType object from the
UpdateInputs list.
The structure in UpdateInputs is equivalent to
configurer.CodeGenerationArguments{3} for the coder configurer
configurer.
Data Types: cell
Object Functions
generateCode | Generate C/C++ code using coder configurer |
generateFiles | Generate MATLAB files for code generation using coder configurer |
validatedUpdateInputs | Validate and extract machine learning model parameters to update |
Examples
Generate Code Using Coder Configurer
Train a machine learning model, and then generate code for the predict and update functions of the model by using a coder configurer.
Load the ionosphere data set, and train a binary linear classification model. Pass the transposed predictor matrix Xnew to fitclinear, and use the 'ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument to specify that the columns of Xnew correspond to observations.
load ionosphere Xnew = X'; Mdl = fitclinear(Xnew,Y,'ObservationsIn','columns');
Mdl is a ClassificationLinear object.
Create a coder configurer for the ClassificationLinear model by using learnerCoderConfigurer. Specify the predictor data Xnew, and use the 'ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument to specify the observation dimension of Xnew. The learnerCoderConfigurer function uses these input arguments to configure the coder attributes of the corresponding input arguments of predict.
configurer = learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,Xnew,'ObservationsIn','columns')
configurer =
ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer with properties:
Update Inputs:
Beta: [1x1 LearnerCoderInput]
Bias: [1x1 LearnerCoderInput]
Prior: [1x1 LearnerCoderInput]
Cost: [1x1 LearnerCoderInput]
Predict Inputs:
X: [1x1 LearnerCoderInput]
ObservationsIn: [1x1 EnumeratedInput]
Code Generation Parameters:
NumOutputs: 1
OutputFileName: 'ClassificationLinearModel'
Properties, Methods
configurer is a ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer object, which is a coder configurer of a ClassificationLinear object.
To generate C/C++ code, you must have access to a C/C++ compiler that is configured properly. MATLAB Coder locates and uses a supported, installed compiler. You can use mex -setup to view and change the default compiler. For more details, see Change Default Compiler.
Generate code for the predict and update functions of the linear classification model (Mdl).
generateCode(configurer)
generateCode creates these files in output folder: 'initialize.m', 'predict.m', 'update.m', 'ClassificationLinearModel.mat'
The generateCode function completes these actions:
Generate the MATLAB files required to generate code, including the two entry-point functions
predict.mandupdate.mfor thepredictandupdatefunctions ofMdl, respectively.Create a MEX function named
ClassificationLinearModelfor the two entry-point functions.Create the code for the MEX function in the
codegen\mex\ClassificationLinearModelfolder.Copy the MEX function to the current folder.
Display the contents of the predict.m, update.m, and initialize.m files by using the type function.
type predict.mfunction varargout = predict(X,varargin) %#codegen
% Autogenerated by MATLAB, 20-Aug-2020 18:27:03
[varargout{1:nargout}] = initialize('predict',X,varargin{:});
end
type update.mfunction update(varargin) %#codegen
% Autogenerated by MATLAB, 20-Aug-2020 18:27:03
initialize('update',varargin{:});
end
type initialize.mfunction [varargout] = initialize(command,varargin) %#codegen
% Autogenerated by MATLAB, 20-Aug-2020 18:27:03
coder.inline('always')
persistent model
if isempty(model)
model = loadLearnerForCoder('ClassificationLinearModel.mat');
end
switch(command)
case 'update'
% Update struct fields: Beta
% Bias
% Prior
% Cost
model = update(model,varargin{:});
case 'predict'
% Predict Inputs: X, ObservationsIn
X = varargin{1};
if nargin == 2
[varargout{1:nargout}] = predict(model,X);
else
PVPairs = cell(1,nargin-2);
for i = 1:nargin-2
PVPairs{1,i} = varargin{i+1};
end
[varargout{1:nargout}] = predict(model,X,PVPairs{:});
end
end
end
Update Parameters of Linear Classification Model in Generated Code
Train a linear classification model using a partial data set and create a coder configurer for the model. Use the properties of the coder configurer to specify coder attributes of the linear model parameters. Use the object function of the coder configurer to generate C code that predicts labels for new predictor data. Then retrain the model using the entire data set, and update parameters in the generated code without regenerating the code.
Train Model
Load the ionosphere data set. This data set has 34 predictors and 351 binary responses for radar returns, either bad ('b') or good ('g'). Train a binary linear classification model using half of the observations. Transpose the predictor data, and use the 'ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument to specify that the columns of XTrain correspond to observations.
load ionosphere rng('default') % For reproducibility n = length(Y); c = cvpartition(Y,'HoldOut',0.5); idxTrain = training(c,1); XTrain = X(idxTrain,:)'; YTrain = Y(idxTrain); Mdl = fitclinear(XTrain,YTrain,'ObservationsIn','columns');
Mdl is a ClassificationLinear object.
Create Coder Configurer
Create a coder configurer for the ClassificationLinear model by using learnerCoderConfigurer. Specify the predictor data XTrain, and use the 'ObservationsIn' name-value pair argument to specify the observation dimension of XTrain. The learnerCoderConfigurer function uses these input arguments to configure the coder attributes of the corresponding input arguments of predict. Also, set the number of outputs to 2 so that the generated code returns predicted labels and scores.
configurer = learnerCoderConfigurer(Mdl,XTrain,'ObservationsIn','columns','NumOutputs',2);
configurer is a ClassificationLinearCoderConfigurer object, which is a coder configurer of a ClassificationLinear object.
Specify Coder Attributes of Parameters
Specify the coder attributes of the linear classification model parameters so that you can update the parameters in the generated code after retraining the model. This example specifies the coder attributes of the predictor data that you want to pass to the generated code.
Specify the coder attributes of the X property of configurer so that the generated code accepts any number of observations. Modify the SizeVector and VariableDimensions attributes. The SizeVector attribute specifies the upper bound of the predictor data size, and the VariableDimensions attribute specifies whether each dimension of the predictor data has a variable size or fixed size.
configurer.X.SizeVector = [34 Inf]; configurer.X.VariableDimensions
ans = 1x2 logical array
0 1
The size of the first dimension is the number of predictor variables. This value must be fixed for a machine learning model. Because the predictor data contains 34 predictors, the value of the SizeVector attribute must be 34 and the value of the VariableDimensions attribute must be 0.
The size of the second dimension is the number of observations. Setting the value of the SizeVector attribute to Inf causes the software to change the value of the VariableDimensions attribute to 1. In other words, the upper bound of the size is Inf and the size is variable, meaning that the predictor data can have any number of observations. This specification is convenient if you do not know the number of observations when generating code.
The order of the dimensions in SizeVector and VariableDimensions depends on the coder attributes of ObservationsIn.
configurer.ObservationsIn
ans =
EnumeratedInput with properties:
Value: 'columns'
SelectedOption: 'Built-in'
BuiltInOptions: {'rows' 'columns'}
IsConstant: 1
Tunability: 1
When the Value attribute of the ObservationsIn property is 'columns', the first dimension of the SizeVector and VariableDimensions attributes of X corresponds to the number of predictors, and the second dimension corresponds to the number of observations. When the Value attribute of ObservationsIn is 'rows', the order of the dimensions is switched.
Generate Code
To generate C/C++ code, you must have access to a C/C++ compiler that is configured properly. MATLAB Coder locates and uses a supported, installed compiler. You can use mex -setup to view and change the default compiler. For more details, see Change Default Compiler.
Generate code for the predict and update functions of the linear classification model (Mdl).
generateCode(configurer)
generateCode creates these files in output folder: 'initialize.m', 'predict.m', 'update.m', 'ClassificationLinearModel.mat'
The generateCode function completes these actions:
Generate the MATLAB files required to generate code, including the two entry-point functions
predict.mandupdate.mfor thepredictandupdatefunctions ofMdl, respectively.Create a MEX function named
ClassificationLinearModelfor the two entry-point functions.Create the code for the MEX function in the
codegen\mex\ClassificationLinearModelfolder.Copy the MEX function to the current folder.
Verify Generated Code
Pass some predictor data to verify whether the predict function of Mdl and the predict function in the MEX function return the same labels. To call an entry-point function in a MEX function that has more than one entry point, specify the function name as the first input argument.
[label,score] = predict(Mdl,XTrain,'ObservationsIn','columns'); [label_mex,score_mex] = ClassificationLinearModel('predict',XTrain,'ObservationsIn','columns');
Compare label and label_mex by using isequal.
isequal(label,label_mex)
ans = logical
1
isequal returns logical 1 (true) if all the inputs are equal. The comparison confirms that the predict function of Mdl and the predict function in the MEX function return the same labels.
Compare score and score_mex.
max(abs(score-score_mex),[],'all')ans = 0
In general, score_mex might include round-off differences compared to score. In this case, the comparison confirms that score and score_mex are equal.
Retrain Model and Update Parameters in Generated Code
Retrain the model using the entire data set.
retrainedMdl = fitclinear(X',Y,'ObservationsIn','columns');
Extract parameters to update by using validatedUpdateInputs. This function detects the modified model parameters in retrainedMdl and validates whether the modified parameter values satisfy the coder attributes of the parameters.
params = validatedUpdateInputs(configurer,retrainedMdl);
Update parameters in the generated code.
ClassificationLinearModel('update',params)Verify Generated Code
Compare the outputs from the predict function of retrainedMdl and the predict function in the updated MEX function.
[label,score] = predict(retrainedMdl,X','ObservationsIn','columns'); [label_mex,score_mex] = ClassificationLinearModel('predict',X','ObservationsIn','columns'); isequal(label,label_mex)
ans = logical
1
max(abs(score-score_mex),[],'all')ans = 0
The comparison confirms that label and label_mex are equal, and that the score values are equal.
More About
LearnerCoderInput Object
A coder configurer uses a LearnerCoderInput object to
specify the coder attributes of predict and update
input arguments.
A LearnerCoderInput object has the following attributes to specify the
properties of an input argument array in the generated code.
| Attribute Name | Description |
|---|---|
SizeVector | Array size if the corresponding
Upper bound of the array
size if the corresponding |
VariableDimensions | Indicator specifying whether each dimension of the array has a
variable size or fixed size, specified as
|
DataType | Data type of the array |
Tunability | Indicator specifying whether or not
If you specify other attribute values when
|
After creating a coder configurer, you can modify the
coder attributes by using dot notation. For example, specify the data type of the bias term
Bias of the coder configurer
configurer:
configurer.Bias.DataType = 'single';Verbose) as true
(default), then the software displays notification messages when you modify the coder
attributes of a machine learning model parameter and the modification changes the coder
attributes of other dependent parameters.EnumeratedInput Object
A coder configurer uses an EnumeratedInput object to specify the coder attributes of predict input arguments that have a finite set of available values.
An EnumeratedInput object has the following attributes to specify the properties of an input argument array in the generated code.
| Attribute Name | Description |
|---|---|
Value | Value of the
The default value of |
SelectedOption | Status of the selected option, specified as
This attribute is read-only. |
BuiltInOptions | List of available character vectors for the corresponding This attribute is read-only. |
IsConstant | Indicator specifying whether or not the array value is a compile-time constant ( If you set this value to |
Tunability | Indicator specifying whether or not If you specify other attribute values when
|
After creating a coder configurer, you can modify the coder attributes by using dot
notation. For example, specify the coder attributes of ObservationsIn of
the coder configurer
configurer:
configurer.ObservationsIn.Value = 'columns';See Also
ClassificationECOCCoderConfigurer | ClassificationLinear | learnerCoderConfigurer | predict | update
Open Example
You have a modified version of this example. Do you want to open this example with your edits?