Implement Pipelining in Simulink
This example shows how to implement pipelining for a system in a Simulink® model. The model consists of an input, functional components applied to the same input, and a concatenated output. For more information on pipelining, see Types of Parallelism.

Setup this model for concurrent execution. To see the completed model, open ex_pipelining_top.
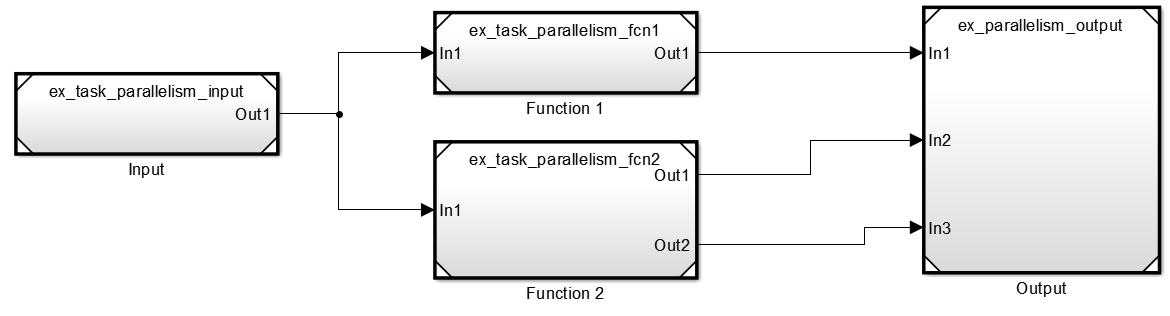
Convert areas in this model to referenced models. Use the same referenced model to replace each of the functional components that process the input. The figure shows a sample configuration.
Open the model configuration parameters for the top level model. Clear the MAT-file logging check box.
On the Solver pane, set Type to
Fixed-stepand click Apply. Also ensure that the Periodic sample time constraint is set toUnconstrained. Under Additional options, select Allow tasks to execute concurrently on target and click Configure Tasks.In the Concurrent Execution dialog box, in the right pane, select the Enable explicit model partitioning for concurrent behavior check box. With explicit partitioning, you can partition your model manually.
In the selection pane, select CPU. Click Add task
 three times to add three new tasks.
three times to add three new tasks.In the selection pane, select Tasks and Mapping. On the Map block to tasks pane:
Under Block: Input, click
select taskand selectPeriodic: Task.Under Block: Function 1, select
Periodic: Task1.Under Block: Function 2, select
Periodic: Task2.Under Block: Output, select
Periodic: Task.
This maps your partitions to the tasks you created. The Input and Output model blocks are on one task. Each functional component is assigned a separate task.
Close the Concurrent Execution dialog box.
Apply these configuration parameters to all referenced models. For more information, see Share a Configuration with Multiple Models.
Update your model to see the tasks mapped to individual model blocks.

Note
Notice that delays are introduced between different tasks, indicated by the z-1 badge. Introducing these delays may cause different model outputs in Simulink. Ensure that your model has an expected output on simulating the parallelized model.