Model
Reference another model to create model hierarchy
- Library:
Simulink / Ports & Subsystems
HDL Coder / Ports & Subsystems
Description
The Model block includes a model as a block in another model. The included model is called a referenced model, and the model that contains the Model block is called the parent model.
The Model block displays input and output ports that correspond to the top-level input and output ports of the referenced model. Using these ports allow you to connect the referenced model to other blocks in the parent model.
By default, you can see the contents of a referenced model by double-clicking the Model block. However, if you have a Simulink® Coder™ license, you can conceal the implementation details of a referenced model by protecting the model. See Protect Models to Conceal Contents (Simulink Coder). If you receive a protected model, see Reference Protected Models from Third Parties.
To specify the referenced model and set simulation parameters, open the Block Parameters dialog box and use the Main tab. To specify instance-specific values for model arguments, use the Instance parameters tab.
Ports
Input
Port_1 — Input port corresponding to root-level blocks of referenced
model
real or complex values of any data type supported by Simulink
The Model block has an input port for each input port of the model it references. The input ports of referenced models are defined by Inport, In Bus Element, Trigger, and Enable blocks. The name of the Model block port matches the name of the corresponding port in the referenced model. The input signal for each Model block port must be valid for the corresponding port in the referenced model. See Model Reference Interface and Boundary.
Input signals can have real or complex values of any data type supported by Simulink, including bus objects, arrays of buses, fixed-point, and enumerated data types. For details about data types, see Data Types Supported by Simulink.
Output
Port_1 — Output port corresponding to root-level blocks of referenced
model
real or complex values of any data type supported by Simulink
The Model block has an output port for each output port of the model it references. The output ports of referenced models are defined by Outport and Out Bus Element blocks. The name of the Model block port matches the name of the corresponding port in the referenced model. The output signals of the Model block are the signals connected to the Outport and Out Bus Element blocks in the referenced model. See Model Reference Interface and Boundary.
Output signals can have real or complex values of any data type supported by Simulink, including bus objects, arrays of buses, fixed-point, and enumerated data types. For details about data types, see Data Types Supported by Simulink.
Parameters
Main
Model name — File name of referenced model
'' (default) | character vector
File name of the referenced model, specified as a character vector. The file extension is optional.
The file name must be a valid MATLAB® identifier for a model, as defined in Model Names.
To navigate to the model that you want to reference, click Browse.
To view the model that you specified, click Open Model.
Programmatic Use
Parameter:
ModelFile |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'' | '<file
name>' |
Default:
'' |
Simulation mode — Simulation mode for model reference
Normal (default) | Accelerator | Software-in-the-loop (SIL) | Processor-in-the-loop (PIL)
Specify the simulation mode for the Model block. The simulation mode for the Model block can be different than the simulation mode of its referenced model and of other models in the model hierarchy.
Accelerator— Create a MEX-file for the referenced model and then execute the referenced model by running the S-function.Normal— Execute the referenced model interpretively, as if the referenced model is an atomic subsystem implemented directly within the parent model.Software-in-the-loop (SIL)— This option requires an Embedded Coder® license. Generate production code based on the Code Interface parameter setting. The code is compiled for, and executed on, the host platform.Processor-in-the-loop (PIL)— This option requires an Embedded Coder license. Generate production code based on the Code Interface parameter setting. This code is compiled for, and executed on, the target platform. A target connectivity API implementation supports the exchange of data between the host and target at each time step during the PIL simulation.
The corners of the Model block indicate the simulation
mode of the Model block. For normal mode, the corners
have empty triangles. For accelerator mode, the corner triangles are
filled in. For SIL and PIL modes, the corners are filled in and the word
(SIL) or (PIL) appears on the
block icon.
Although you can specify any simulation mode for a model, when you reference that model, the Model block specifies the simulation mode of the referenced model instance. The simulation mode of a parent model can override the simulation mode of a Model block. See Overridden Simulation Modes.
Programmatic Use
Parameter:
SimulationMode |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'Normal' |
'Accelerator' |
'Software-in-the-loop' |
'Processor-in-the-loop' |
Default:
'Normal' |
Code interface — Generate code from top model or referenced model
Model reference (default) | Top model
Specify whether to generate the code from the top model or the
referenced model for SIL and PIL simulation modes. To deploy the
generated code as part of a larger application that uses the referenced
model, specify Model reference. To deploy the
generated code as a standalone application, specify Top
model.
Model referenceThe code is generated from the referenced model as part of a model hierarchy. Code generation uses the
slbuild('command.model', 'ModelReferenceCoderTarget')Top modelThe code is generated from the top model with the standalone code interface. Code generation uses the
slbuild('command.model')
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, set Simulation mode
to either Software-in-the-loop (SIL) or
Processor-in-the-loop (PIL).
Programmatic Use
Parameter:
CodeInterface |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'Model reference' | 'Top
model' |
Default:
'Model reference' |
Show model initialize port — Control display of initialize event port
off (default) | on
Control the display of the initialize event port on the Model block.
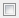 off
offRemove the port.
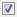 on
onDisplay the model initialize event port.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ShowModelInitializePort |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'off' | 'on' |
Default:
'off' |
Show model reset ports — Control display of reset event ports
off (default) | on
Control the display of the reset event ports on the Model block.
 off
offRemove the ports.
 on
onDisplay the model reset event ports.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, add a Reset Function block to the referenced model. To specify the port name, use the Event name parameter of the Event Listener block in the Reset Function block.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ShowModelResetPorts |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'off' | 'on' |
Default:
'off' |
Show model terminate port — Control display of terminate event port
off (default) | on
Control the display of the terminate event port on the Model block.
 off
offRemove the port.
 on
onDisplay the model terminate event port.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Show model initialize port.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ShowModelTerminatePort |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'off' | 'on' |
Default:
'off' |
Schedule rates — Control display of periodic event ports
off (default) | on
Control the display of the periodic event ports on the Model block.
 off
offHide the ports.
 on
onDisplay the ports for rate-based models. A rate-based model is a model with the Sample time for a connected Inport block specified.
If you want to manually specify the port rates, set the parameter
AutoFillPortDiscreteRatesto'off', and then add the port rates to the parameterPortDiscreteRates.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ScheduleRates |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'off' | 'on' |
Default:
'off' |
Schedule rates with — Control display of periodic event ports
Ports (default) | Schedule Editor
Control display of periodic event ports on Model block.
PortsDisplay ports for rate-based models.
Schedule EditorCreate partitions for rate-based models.
Dependencies
To enable this parameter, select Schedule rates.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ScheduleRatesWith |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'Ports' |
'ScheduleEditor' |
Default:
'Ports' |
Instance Parameters
Instance parameters — Display instance parameters and specify values for referenced
model
number | workspace variable | mathematical expression | structure or structure field
Display instance parameters and specify instance-specific values. Instance parameters are block parameters that have been configured in the referenced model to use a different value for each instance of the model.
To specify instance-specific values, use the Value column in the table. To specify that a parameter value can be overridden by the parent model, select the Argument check box. For more information about configuring instance parameters in a referenced model and specifying instance-specific values at the Model block, see Parameterize Instances of a Reusable Referenced Model.
When changing instance-specific values, you can use a partial structure that has fields that correspond to only the instance parameters whose values you want to change. Instance parameters not included in the partial structure retain their values. In the structure, include the instance parameter names and values, specified as character vectors.
Programmatic Use
Block parameter:
ParameterArgumentValues |
| Type: structure |
| Value: structure |
| Default: structure with no fields |
Block parameter:
InstanceParameters |
| Type: structure array |
Value: structure with
fields: Name, Value,
Path, and
Argument. |
Model Examples
Block Characteristics
Data Types |
|
Direct Feedthrough |
|
Multidimensional Signals |
|
Variable-Size Signals |
|
Zero-Crossing Detection |
|
[a] Actual data type or capability support depends on block implementation. | |
Compatibility Considerations
Specifying variant models in Model blocks is no longer supported
Warns starting in R2019a
Starting in R2019a, specifying variant models in Model blocks is no longer supported. The Model Variants block, which was a Model block preconfigured to specify variant models, is also no longer supported. Loading a model that contains these blocks converts them to Variant Subsystem blocks that contain Model blocks that represent the variant choices.
Variant Subsystem blocks provide these advantages:
You can mix Model blocks and Subsystem blocks as variant choices.
You can specify variants that have different numbers of input and output ports.
The Variant Subsystem block parameter Analyze all choices during update diagram and generate preprocessor conditionals behaves differently from the Model block parameter Generate preprocessor conditionals. Instead of causing simulation and update diagram to compile the active variant only, the Variant Subsystem block parameter compiles all variants.
If you have scripts that use Model block parameters for variants, you must update them to use Variant Subsystem block parameters.
Extended Capabilities
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using Simulink® Coder™.
Actual code generation support depends on block implementation.
HDL Code Generation
Generate Verilog and VHDL code for FPGA and ASIC designs using HDL Coder™.
HDL Coder™ provides additional configuration options that affect HDL implementation and synthesized logic. For more information about using the Model block for HDL code generation and best practices and limitations, see Model Referencing for HDL Code Generation (HDL Coder).
See also Generate Black Box Interface for Referenced Model (HDL Coder) and Generate Parameterized Code for Referenced Models (HDL Coder).
| Architecture | Description |
|---|---|
ModelReference (default) | When you want to generate code from a referenced model and
any nested models, use the
ModelReference implementation.
For more information, see How To Generate Code for a Referenced Model (HDL Coder). |
BlackBox | Use the For more information, see Generate Black Box Interface for Referenced Model (HDL Coder). |
For the BlackBox architecture, you
can customize port names and set attributes of the external component
interface. See Customize Black Box or HDL Cosimulation Interface (HDL Coder).
| BalanceDelays | Detects introduction of new delays along one path and inserts
matching delays on the other paths. The default is |
| ConstrainedOutputPipeline | Number of registers to place at
the outputs by moving existing delays within your design. Distributed
pipelining does not redistribute these registers. The default is
|
| DistributedPipelining | Pipeline register distribution, or register retiming. The default
is |
| DSPStyle | Synthesis attributes for multiplier mapping. The default is |
| InputPipeline | Number of input pipeline stages
to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained
output pipelining can move these registers. The default is
|
| OutputPipeline | Number of output pipeline stages
to insert in the generated code. Distributed pipelining and constrained
output pipelining can move these registers. The default is
|
| ReferenceModelPrefix | Prefix of the referenced model to insert in the generated code.
The code generator applies this prefix to submodel file names and
HDL identifiers. The default prefix is Note
|
| SharingFactor | Number of functionally equivalent resources to map to a single shared resource. The default is 0. See also Resource Sharing (HDL Coder). |
| StreamingFactor | Number of parallel data paths, or vectors, that are time multiplexed to transform into serial, scalar data paths. The default is 0, which implements fully parallel data paths. See also Streaming (HDL Coder). |
Fixed-Point Conversion
Design and simulate fixed-point systems using Fixed-Point Designer™.
Actual data type support depends on block implementation.



