Verify HDL Module with MATLAB Test Bench
Tutorial Overview
This tutorial guides you through the basic steps for setting up an HDL Verifier™ application that uses MATLAB® to verify a simple HDL design. In this tutorial, you develop, simulate, and verify a model of a pseudorandom number generator based on the Fibonacci sequence. The model is coded in VHDL®.
Note
This tutorial demonstrates creating and running a test bench using ModelSim® SE 6.5. If you are not using this version, the messages and screen images from ModelSim may not appear to you exactly as they do in this tutorial.
This tutorial requires MATLAB, the HDL Verifier software, and the ModelSim HDL simulator.
In this tutorial, you will perform the following steps:
Set Up Tutorial Files
To help others have access to copies of the tutorial files, set up a folder for your own tutorial work:
Create a folder outside the scope of your MATLAB installation folder into which you can copy the tutorial files. The folder must be writable. This tutorial assumes that you create a folder named
MyPlayArea.Copy the following files to the folder you just created:
matlabroot\toolbox\edalink\extensions\modelsim\modelsimdemos\modsimrand_plot.mmatlabroot\toolbox\edalink\extensions\modelsim\modelsimdemos\VHDL\modsimrand\modsimrand.vhd
Start the MATLAB Server
This section describes starting MATLAB, setting up the current folder for completing the tutorial, starting the MATLAB server component, and checking for client connections, using shared memory or TCP/IP socket mode. These instructions assume you are familiar with the MATLAB user interface.
Perform the following steps:
Start MATLAB.
Set your MATLAB current folder to the folder you created in Set Up Tutorial Files.
Verify that the MATLAB server is running by calling function
hdldaemonwith the'status'option in the MATLAB Command Window as shown here:hdldaemon('status')If the server is not running, the function displays
HDLDaemon is NOT running
If the server is running in TCP/IP socket mode, the message reads
HDLDaemon socket server is running on Port portnum with 0 connectionsIf the server is running in shared memory mode, the message reads
HDLDaemon shared memory server is running with 0 connections
If the server is not currently running, skip to step
5.Shut down the server by typing
hdldaemon('kill')You will see the following message that confirms that the server was shut down.
HDLDaemon server was shutdown
Start the server in TCP/IP socket mode by calling
hdldaemonwith the property name/property value pair'socket' 0. The value 0 specifies that the operating system assign the server a TCP/IP socket port that is available on your system. For examplehdldaemon('socket', 0)The server informs you that it has started by displaying the following message. The
portnumwill be specific to your system:HDLDaemon socket server is running on Port portnum with 0 connections
Make note of
portnumas you will need it when you issue thematlabtbcommand in Load Simulation.You can alternatively specify that the MATLAB server use shared memory communication instead of TCP/IP socket communication; however, for this tutorial we will use socket communication as means of demonstrating this type of connection. For details on how to specify the various options, see the description of
hdldaemon.
Start ModelSim Simulator and Set Up for Cosimulation
This section describes the basic procedure for starting the ModelSim software and setting up a ModelSim design library. These instructions assume you are familiar with the ModelSim user interface.
Perform the following steps:
Start ModelSim from the MATLAB environment by calling the function
vsimin the MATLAB Command Window.vsim
This function launches and configures ModelSim for use with the HDL Verifier software. The first folder of ModelSim matches your MATLAB current folder.
Verify the current ModelSim folder. You can verify that the current ModelSim folder matches the MATLAB current folder by entering the
lscommand in the ModelSim command window.
The command should list the files
modsimrand.vhd,modsimrand_plot.m,transcript, andcompile_and_launch.tcl.If it does not, change your ModelSim folder to the current MATLAB folder. You can find the current MATLAB folder by looking in the Current Folder Browser or by viewing the Current folder navigation bar. In ModelSim, you can change the working folder by issuing the command
cd directory
Where
directoryis the folder you want to work from. Or you may also change directory by selecting File > Change Directory....Create a design library to hold your compilation results. To create the library and required
_infofile, enter thevlibandvmapcommands as follows:ModelSim> vlib work ModelSim> vmap work work

Note
You must use the ModelSim File menu or
vlibcommand to create the library folder so that the required_infofile is created. Do not create the library with operating system commands.
Develop VHDL Code
After setting up a design library, typically you would use the ModelSim Editor
to create and modify your HDL code. For this tutorial, you do not
need to create the VHDL code yourself. Instead, open and examine
the existing file modsimrand.vhd. This section
highlights areas of code in modsimrand.vhd that
are of interest for a ModelSim and MATLAB test bench.
If you choose not to examine the HDL code at this time, skip to Compile VHDL Code.
You can open modsimrand.vhd in the edit window with the
edit command, as follows:
ModelSim> edit modsimrand.vhd
ModelSim opens its edit window and
displays the VHDL code for modsimrand.vhd.
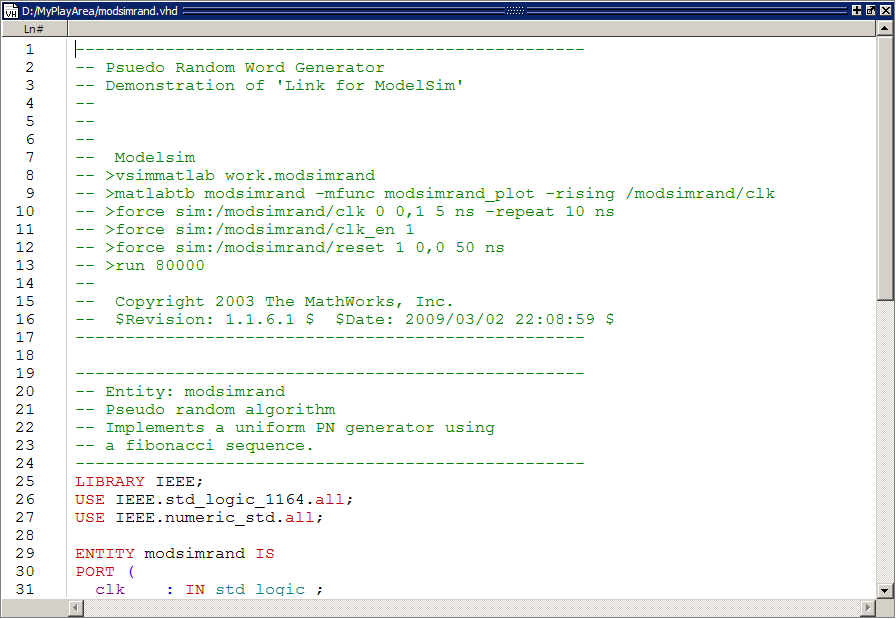
While you are viewing the file, note the following:
The line
ENTITY modsimrandcontains the definition for the VHDL entitymodsimrand:ENTITY modsimrand IS PORT ( clk : IN std_logic ; clk_en : IN std_logic ; reset : IN std_logic ; dout : OUT std_logic_vector (31 DOWNTO 0); END modsimrand;
This is the entity that will be verified in the MATLAB environment during the tutorial. Note the following:
By default, the MATLAB server assumes that the name of the MATLAB function that verifies the entity in the MATLAB environment is the same as the entity name. You have the option of naming the MATLAB function explicitly. However, if you do not specify a name, the server expects the function name to match the entity name. In this example, the MATLAB function name is
modsimrand_plotand does not match.The entity must be defined with a
PORTclause that includes at least one port definition. Each port definition must specify a port mode (IN,OUT, orINOUT) and a VHDL data type that is supported by the HDL Verifier software.The entity
modsimrandin this example is defined with three input portsclk,clk_en, andresetof typeSTD_LOGICand output portdoutof typeSTD_LOGIC_VECTOR. The output port passes simulation output data out to the MATLAB function for verification. The optional input ports receive clock and reset signals from the function. Alternatively, the input ports can receive signals from ModelSimforcecommands.For more information on coding port entities for use with MATLAB, see Coding HDL Modules for Verification with MATLAB.
The remaining code for
modsimrand.vhddefines a behavioral architecture formodsimrandthat writes a randomly generated Fibonacci sequence to an output register when the clock experiences a rising edge.
When you are finished examining the file, close the ModelSim edit window.
Compile VHDL Code
After you create or edit your VHDL source files, compile
them. As part of this tutorial, compile modsimrand.vhd.
One way of compiling the file is to click the file name in the project
workspace and select Compile > Compile All. An alternative
is to specify modsimrand.vhd with the vcom command,
as follows:
ModelSim> vcom modsimrand.vhd
If the compilation succeeds, messages appear in the command window and the compiler populates the work library with the compilation results.
Develop MATLAB Function
The HDL Verifier software verifies HDL hardware in MATLAB as
a function. Typically, at this point you would create or edit a MATLAB function
that meets HDL Verifier requirements. For this tutorial,
you do not need to develop the MATLAB test bench function yourself.
Instead, open and examine the existing file modsimrand_plot.m.
If you choose not to examine the HDL code at this time, skip to Load Simulation.
Note
modsimrand_plot.m is a lower-level component
of the MATLAB Random Number Generator example. Plotting code
within modsimrand_plot.m is not discussed in the
next section. This tutorial focuses only on those parts of modsimrand_plot.m that
are required for MATLAB to verify a VHDL model.
You can open modsimrand_plot.m in the MATLAB Editor.
For example:
edit modsimrand_plot.m
While you are viewing the file, note the following:
On line 1, you will find the MATLAB function name specified along with its required parameters:
function [iport,tnext] = modsimrand_plot(oport,tnow,portinfo)
This function definition is significant because it represents the communication channel between MATLAB and ModelSim. Note:
When coding the function, you must define the function with two output parameters,
iportandtnext, and three input parameters,oport,tnow, andportinfo. See MATLAB Function Syntax and Function Argument Definitions.You can use the
iportparameter to drive input signals instead of, or in addition to, using other signal sources, such as ModelSimforcecommands. Depending on your application, you might use any combination of input sources. However, if multiple sources drive signals to a singleiport, you will need a resolution function to handle signal contention.
On lines 22 and 23, you will find some parameter initialization:
tnext = []; iport = struct();
In this case, function outputs
iportandtnextare initialized to empty values.When coding a MATLAB function for use with HDL Verifier, you need to know the types of the data that the test bench function receives from and needs to return to ModelSim and how HDL Verifier handles this data; see Supported Data Types. This function includes the following port data type definitions and conversions:
The entity defined for this tutorial consists of three input ports of type
STD_LOGICand an output port of typeSTD_LOGIC_VECTOR.Data of type
STD_LOGIC_VECTORconsists of a column vector of characters with one bit per character.The interface converts scalar data of type
STD_LOGICto a character that matches the character literal for the corresponding enumerated type.
On line 62, the line of code containing
oport.doutshows how the data that a MATLAB function receives from ModelSim might need to be converted for use in the MATLAB environment:ud.buffer(cyc) = mvl2dec(oport.dout)
In this case, the function receives
STD_LOGIC_VECTORdata onoport. The functionmvl2decconverts the bit vector to a decimal value that can be used in arithmetic computations. Supported Data Types provides a summary of the types of data conversions to consider when coding your own MATLAB functions.Feel free to browse through the rest of
modsimrand_plot.m. When you are finished, go to Load Simulation.
Load Simulation
After you compile the VHDL source file, you are ready to
load the model for simulation. This section explains how to load an
instance of entity modsimrand for simulation:
Load the instance of
modsimrandfor verification. To load the instance, specify thevsimmatlabcommand as follows:ModelSim> vsimmatlab modsimrand
The
vsimmatlabcommand starts the ModelSim simulator,vsim, specifically for use with MATLAB. ModelSim displays a series of messages in the command window as it loads the entity's packages and architecture.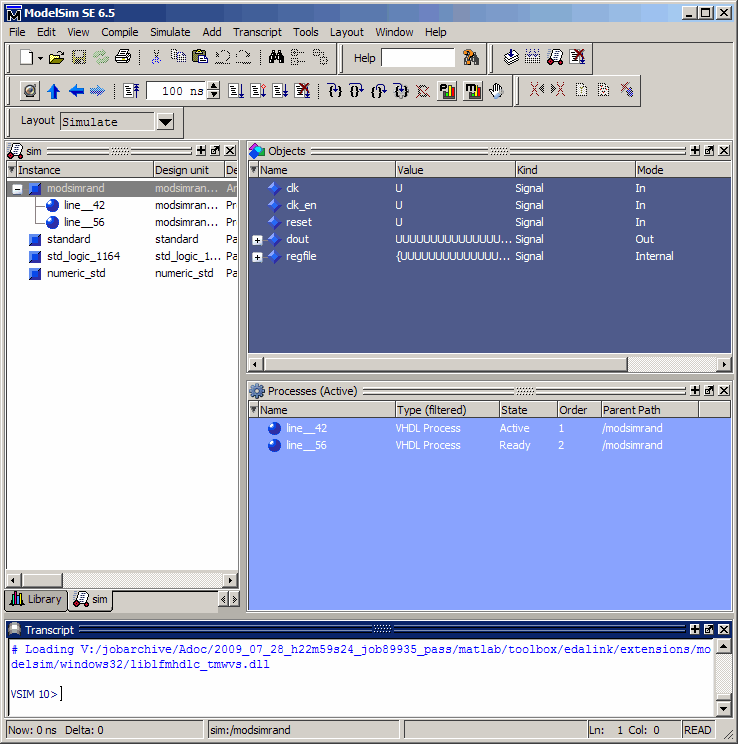
Initialize the simulator for verifying
modsimrandwith MATLAB. You initialize ModelSim by using the HDL Verifiermatlabtbcommand. This command defines the communication link and a callback to a MATLAB function that executes in MATLAB on behalf of ModelSim. In addition, thematlabtbcommand can specify parameters that control when the MATLAB function executes.For this tutorial, enter the following
matlabtbcommand:> matlabtb modsimrand -mfunc modsimrand_plot -rising /modsimrand/clk -socket portnumArguments in the command line specify the following conditions:
modsimrand— Specifies the VHDL module to cosimulate.-mfunc modsimrand_plot— Links an instance of the entitymodsimrandto the MATLAB functionmodsimrand_plot.m. The argument is required because the entity name is not the same as the test bench function name.-rising /modsimrand/clk— Specifies that the test bench function be called whenever signal/modsimrand/clkexperiences a rising edge.-socketportnum— Specifies the port number issued with or returned by the call tohdldaemonin Start the MATLAB Server.
Initialize clock and reset input signals. You can drive simulation input signals using several mechanisms, including ModelSim
forcecommands and aniportparameter (see Syntax of a Test Bench Function). For now, enter the followingforcecommands:> force /modsimrand/clk 0 0 ns, 1 5 ns -repeat 10 ns > force /modsimrand/clk_en 1 > force /modsimrand/reset 1 0, 0 50 ns
The first command forces the
clksignal to value 0 at 0 nanoseconds and to 1 at 5 nanoseconds. After 10 nanoseconds, the cycle starts to repeat every 10 nanoseconds. The second and thirdforcecommands setclk_ento 1 andresetto 1 at 0 nanoseconds and to 0 at 50 nanoseconds.
The ModelSim environment is ready to run a simulation. Now, you need to set up the MATLAB function.
Run Simulation
This section explains how to start and monitor this simulation, and rerun it, if you desire. When you have completed as many simulation runs as desired, shut down the simulation as described in the next section.
Running the Simulation for the First Time
Before running the simulation for the first time, you must verify the client connection. You may also want to set breakpoints for debugging.
Perform the following steps:
Open ModelSim and MATLAB windows.
In MATLAB, verify the client connection by calling
hdldaemonwith the'status'option:hdldaemon('status')This function returns a message indicating a connection exists:
HDLDaemon socket server is running on port 4795 with 1 connection
Or
HDLDaemon shared memory server is running with 1 connection
Note
If you attempt to run the simulation before starting the
hdldaemonin MATLAB, you will receive the following warning:#ML Warn - MATLAB server not available (yet), The entity 'modsimrand' will not be active
Open
modsimrand_plot.min the MATLAB Editor.Search for
oport.doutand set a breakpoint at that line by clicking next to the line number. A red breakpoint marker will appear.Return to ModelSim and enter the following command in the command window:
> run 80000
This command instructs ModelSim to advance the simulation 80,000 time steps (80,000 nanoseconds using the default time step period). Because you previously set a breakpoint in
modsimrand_plot.m, however, the simulation runs in MATLAB until it reaches the breakpoint.ModelSim is now blocked and remains blocked until you explicitly unblock it. While the simulation is blocked, note that MATLAB displays the data that ModelSim passed to the MATLAB function in the Workspace window.
In ModelSim, an empty figure window opens. You can use this window to plot data generated by the simulation.
Examine
oport,portinfo, andtnowby hovering over these arguments inside the MATLAB Editor. Observe thattnow, the current simulation time, is set to0. Also notice that, because the simulation has reached a breakpoint during the first call tomodsimrand_plot, theportinfoargument is visible in the MATLAB workspace.Click Continue in the MATLAB Editor. The next time the breakpoint is reached, notice that
portinfono longer appears in the MATLAB workspace. Theportinfofunction does not show because it is passed in only on the first function invocation. Also note that the value oftnowadvances from 0 to 5e-009.Clear the breakpoint by clicking the red breakpoint marker.
Unblock ModelSim and continue the simulation by clicking Continue in the MATLAB Editor.
The simulation runs to completion. As the simulation progresses, it plots generated data in a figure window. When the simulation completes, the figure window appears as shown here.
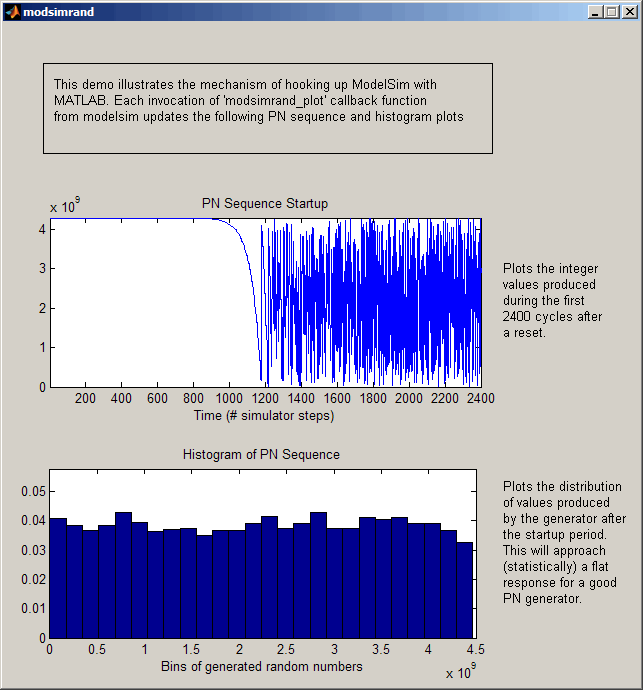
The simulation runs in MATLAB until it reaches the breakpoint that you just set. Continue the simulation/debugging session as desired.
Rerunning the Simulation
If you want to run the simulation again, you must restart the simulation in ModelSim, reinitialize the clock, and reset input signals. To do so:
Close the figure window.
Restart the simulation with the following command:
> restart
The Restart dialog box appears. Leave all the options enabled, and click Restart.
Note
The Restart button clears the simulation context established by a
matlabtbcommand. Thus, after restarting ModelSim, you must reissue the previous command or issue a new command.Reissue the
matlabtbcommand in the HDL simulator.> matlabtb modsimrand -mfunc modsimrand_plot -rising /modsimrand/clk -socketportnumOpen
modsimrand_plot.min the MATLAB Editor.Set a breakpoint at the same line as in the previous run.
Return to ModelSim and re-enter the following commands to reinitialize clock and input signals:
> force /modsimrand/clk 0 0,1 5 ns -repeat 10 ns > force /modsimrand/clk_en 1 > force /modsimrand/reset 1 0, 0 50 ns
Enter a command to start the simulation, for example:
> run 80000
Shut Down Simulation
This section explains how to shut down a simulation in an orderly way.
In ModelSim, perform the following steps:
Stop the simulation on the client side by selecting Simulate > End Simulation or entering the
quitcommand.Quit ModelSim.
In MATLAB, you can just quit the application, which will shut down the simulation and also close MATLAB.
To shut down the server without closing MATLAB, you have
the option of calling hdldaemon with the 'kill' option:
hdldaemon('kill')The following message appears, confirming that the server was shut down:
HDLDaemon server was shutdown