Cumulative Product
Cumulative product of channel, column, or row elements
Library
Math Functions / Math Operations
dspmathops
Description
The Cumulative Product block computes the cumulative product along the specified dimension of the input or across time (running product).
The input can be a vector or matrix.
Input and Output Characteristics
The Cumulative Product block accepts vector or matrix inputs containing real or complex values.
The optional reset port, Rst, accepts scalar values, which
can be any built-in Simulink® data type including boolean. The rate of the
input to the Rst port must be the same or slower than that of the input data
signal. The sample time of the input to the Rst port must be a positive integer
multiple of the input sample time.
Computing the Running Product Along Channels of the Input
When you set the Multiply input along parameter to
Channels (running product), the block computes the
cumulative product of the elements in each input channel. The running product of the
current input takes into account the running product of all previous inputs. In this
mode, you must also specify a value for the Input processing
parameter. When you set the Input processing parameter to
Columns as channels (frame based), the block computes
the running product along each column of the current input. When you set the
Input processing parameter to Elements as
channels (sample based), the block computes a running product for
each element of the input across time. See the following sections for more
information:
When you set the Input processing parameter to
Columns as channels (frame based), the block
treats each input column as an independent channel. As the following figure and
equation illustrate, the output has the following characteristics:
The first row of the first output is the same as the first row of the first input.
The first row of each subsequent output is the element-wise product of the first row of the current input (time t), and the last row of the previous output (time t - Tf, where Tf is the frame period).
The output has the same size, dimension, data type, and complexity as the input.
Given an M-by-N matrix input, u, the output, y, is an M-by-N matrix whose first row has elements

When you set the Input processing parameter to
Elements as channels (sample based), the block
treats each element of the input matrix as an independent channel. As the
following figure and equation illustrate, the output has the following
characteristics:
The first output is the same as the first input.
Each subsequent output is the element-wise product of the current input (time t) and the previous output (time t - Ts, where Ts is the sample period).
The output has the same size, dimension, data type, and complexity as the input.
Given an M-by-N matrix input, u, the output, y, is an M-by-N matrix with the elements
For convenience, the block treats length-M unoriented vector inputs as M-by-1 column vectors when multiplying along channels. In such cases, the output is a length-M unoriented vector.

When you are computing the running product, you can configure the block to
reset the running product whenever it detects a reset event at the optional
Rst port. The rate of the input to the Rst port must be
the same or slower than that of the input data signal. The sample time of the
input to the Rst port must be a positive integer multiple of the input sample
time. The input to the Rst port can be of the Boolean data
type.
If a reset event occurs while the block is performing sample-based processing, the block initializes the current output to the values of the current input. If a reset event occurs while the block is performing frame-based processing, the block initializes the first row of the current output to the values in the first row of the current input.
The Reset port parameter specifies the reset event, which can be one of the following:
Nonedisables theRstport.Rising edge— Triggers a reset operation when theRstinput does one of the following:Rises from a negative value to a positive value or zero
Rises from zero to a positive value, where the rise is not a continuation of a rise from a negative value to zero (see the following figure)

Falling edge— Triggers a reset operation when theRstinput does one of the following:Falls from a positive value to a negative value or zero
Falls from zero to a negative value, where the fall is not a continuation of a fall from a positive value to zero (see the following figure)

Either edge— Triggers a reset operation when theRstinput is aRising edgeorFalling edge(as described above)Non-zero sample— Triggers a reset operation at each sample time that theRstinput is not zero
Note
When you run simulations in Simulink
MultiTasking mode, reset signals have a
one-sample latency. When the block detects a reset event, a one-sample delay
occurs at the reset port rate before the block applies the reset. For more
information on latency and the Simulink tasking modes, see Excess Algorithmic Delay (Tasking Latency) and Time-Based Scheduling and Code Generation (Simulink Coder).
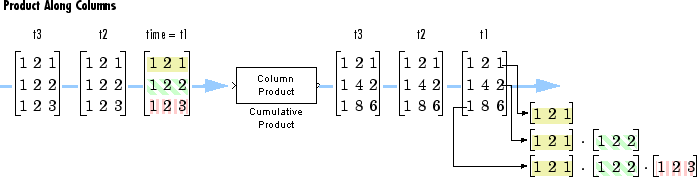
Multiplying Along Columns
When you set the Multiply input along parameter to
Columns, the block computes the cumulative product of
each column of the input. In this mode, the current cumulative product is
independent of the cumulative products of previous inputs.
y = cumprod(u) % Equivalent MATLAB code
The output has the same size, dimension, data type, and complexity as the input. The mth output row is the element-wise product of the first m input rows.
Given an M-by-N input, u, the output, y, is an M-by-N matrix whose jth column has elements
When multiplying along columns, the block treats length-M unoriented vector inputs as M-by-1 column vectors.
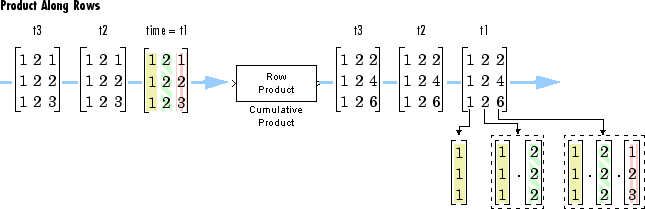
Multiplying Along Rows
When you set the Multiply input along parameter to
Rows, the block computes the cumulative product of
the row elements. In this mode, the current cumulative product is independent of the
cumulative products of previous inputs.
y = cumprod(u,2) % Equivalent MATLAB code
The output has the same size, dimension, and data type as the input. The nth output column is the element-wise product of the first n input columns.
Given an M-by-N matrix input, u, the output, y, is an M-by-N matrix whose ith row has elements
When you multiply along rows, the block treats length-N unoriented vector inputs as 1-by-N row vectors.
Fixed-Point Data Types
The following diagram shows the data types used within the Cumulative Product block for fixed-point signals.
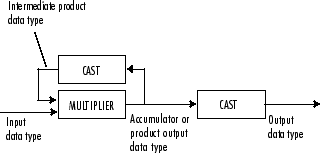
The output of the multiplier is in the product output data type when at least one of the inputs to the multiplier is real. When both of the inputs to the multiplier are complex, the result of the multiplication is in the accumulator data type. For details on the complex multiplication performed, see Multiplication Data Types. You can set the accumulator, product output, intermediate product, and output data types in the block dialog as discussed in Parameters.
Parameters
Main Tab
- Multiply input along
Specify the dimension along which to compute the cumulative product. You can choose to multiply along
Channels (running product),Columns, orRows. For more information, see the following sections:- Input processing
Specify how the block should process the input when computing the running product along the channels of the input. You can set this parameter to one of the following options:
Columns as channels (frame based)— When you select this option, the block treats each column of the input as a separate channel.Elements as channels (sample based)— When you select this option, the block treats each element of the input as a separate channel.
This parameter is available only when you set the Multiply input along parameter to
Channels (running product).- Reset port
Determines the reset event that causes the block to reset the product along channels. The rate of the input to the Rst port must be the same or slower than that of the input data signal. The sample time of the input to the Rst port must be a positive integer multiple of the input sample time. This parameter appears only when you set the Multiply input along parameter to
Channels (running product). For more information, see Resetting the Running Product.
Data Types Tab
Note
Floating-point inheritance takes precedence over the data type settings defined on this pane. When inputs are floating point, the block ignores these settings, and all internal data types are floating point.
- Rounding mode
Specify the rounding mode for fixed-point operations as one of the following:
FloorCeilingConvergentNearestRoundSimplestZero
For more details, see rounding mode.
- Saturate on integer overflow
When you select this parameter, the block saturates the result of its fixed-point operation. When you clear this parameter, the block wraps the result of its fixed-point operation. For details on
saturateandwrap, see overflow mode for fixed-point operations.- Intermediate product
Specify the intermediate product data type. As shown in Fixed-Point Data Types, the output of the multiplier is cast to the intermediate product data type before the next element of the input is multiplied into it. You can set it to:
A rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as inputAn expression that evaluates to a valid data type, for example,
fixdt([],16,0)
Click the Show data type assistant button
 to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the Product
output parameter.
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the Product
output parameter.See Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink) for more information.
- Product output
Specify the product output data type. See Fixed-Point Data Types and Multiplication Data Types for illustrations depicting the use of the product output data type in this block. You can set it to:
A rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as inputAn expression that evaluates to a valid data type, for example,
fixdt([],16,0)
Click the Show data type assistant button
 to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the Product
output parameter.
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the Product
output parameter.See Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink) for more information.
- Accumulator
Specify the accumulator data type. See Fixed-Point Data Types for illustrations depicting the use of the accumulator data type in this block. You can set this parameter to:
A rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as inputA rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as product outputAn expression that evaluates to a valid data type, for example,
fixdt([],16,0)
Click the Show data type assistant button
 to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the
Accumulator parameter.
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the
Accumulator parameter.See Specify Data Types Using Data Type Assistant (Simulink) for more information.
- Output
Specify the output data type. See Fixed-Point Data Types for illustrations depicting the use of the output data type in this block. You can set it to:
A rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as inputA rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as product outputAn expression that evaluates to a valid data type, for example,
fixdt([],16,0)
If both inputs are unsigned, all data types including the output data type is unsigned. If one of the inputs is signed, internal and output data types are signed.
Click the Show data type assistant button
 to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the
Output parameter.
to display the Data Type
Assistant, which helps you set the
Output parameter.See Control Signal Data Types (Simulink) for more information.
- Minimum
Specify the minimum value that the block should output. The default value is
[](unspecified). Simulink uses this value to perform:Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink))
Automatic scaling of fixed-point data types
- Maximum
Specify the maximum value that the block should output. The default value is
[](unspecified). Simulink uses this value to perform:Simulation range checking (see Specify Signal Ranges (Simulink))
Automatic scaling of fixed-point data types
- Lock data type settings against changes by the fixed-point tools
Select this parameter to prevent the fixed-point tools from overriding the data types you specify on the block mask.
Supported Data Types
| Input and Output Ports | Supported Data Types |
|---|---|
Data input port, |
|
Reset input port, | All built-in Simulink data types:
|
Output port |
|
