rectangularArray
Create rectangular antenna array
Description
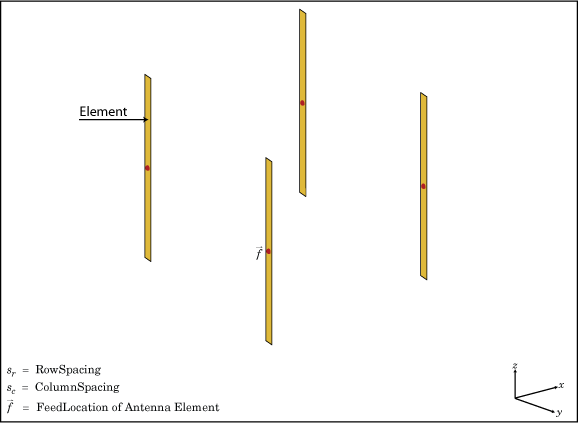
The rectangularArray class creates a rectangular antenna
array in the X-Y plane. By default, the rectangular array is a four-element dipole array
in a 2 x 2 rectangular lattice. The dipoles are center-fed. Each dipole resonates at 70
MHz when isolated.
Creation
Description
array = rectangularArray(Name,Value)Name is the
property name and Value is the corresponding value. You
can specify several name-value pair arguments in any order as
Name1, Value1,
..., NameN, ValueN.
Properties not specified retain default values.
Output Arguments
Properties
Object Functions
show | Display antenna or array structure; display shape as filled patch |
info | Display information about antenna or array |
beamwidth | Beamwidth of antenna |
charge | Charge distribution on metal or dielectric antenna or array surface |
correlation | Correlation coefficient between two antennas in array |
current | Current distribution on metal or dielectric antenna or array surface |
design | Design prototype antenna or arrays for resonance at specified frequency |
EHfields | Electric and magnetic fields of antennas; Embedded electric and magnetic fields of antenna element in arrays |
impedance | Input impedance of antenna; scan impedance of array |
layout | Display array or PCB stack layout |
mesh | Mesh properties of metal or dielectric antenna or array structure |
meshconfig | Change mesh mode of antenna structure |
optimize | Optimize antenna or array using SADEA optimizer |
pattern | Radiation pattern and phase of antenna or array; Embedded pattern of antenna element in array |
patternAzimuth | Azimuth pattern of antenna or array |
patternElevation | Elevation pattern of antenna or array |
returnLoss | Return loss of antenna; scan return loss of array |
sparameters | S-parameter object |
Examples
References
[1] Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory. Analysis and Design, 3rd Ed. New York: Wiley, 2005.
See Also
circularArray | conformalArray | infiniteArray | linearArray



