Mask Editor Overview
A mask is a custom user interface for a block that hides the block's contents, making it appear to the user as an atomic block with its own icon and parameter dialog box.
The Mask Editor dialog box helps you create and customize the block mask. The Mask Editor dialog box opens when you create or edit a mask. You can access the Mask Editor dialog box by any of these options:
To create mask,
In the Modeling tab, under Component, click Create Model Mask.
Select the block and on the Block tab, in the Mask group, click Create Mask. The Mask Editor opens.
To edit mask,
On the Block tab, in the Mask group, click Edit Mask.
Right-click the block and select Mask > Edit Mask.
Note
You can also use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + M to open Mask Editor.
The Mask Editor dialog box contains a set of tabbed panes, each of which enables you define a feature of the mask. These tabs are:
Icon & Ports Pane: To create block mask icons.
Parameters & Dialog Pane: To design mask dialog boxes.
Initialization Pane: To initialize a masked block using MATLAB® code.
Documentation Pane: To add description and help about the block mask.
Note
For information on creating and editing a block mask from command line, see Control Masks Programmatically.
Icon & Ports Pane
The Icon & Ports pane helps you to create a block icon that contains descriptive text, state equations, image, and graphics.
![]()
The Icon & Ports pane is divided into these sections:
Options: Provides a list of different controls that can be applied on the mask icon.
Preview: Displays the preview of the block mask icon.
Icon drawing commands: Enables you to draw mask icon by using MATLAB code.
Note
You can create static and dynamic block mask icon. For more information, see Draw Mask Icon and slexMaskDisplayAndInitializationExample.
Options
Options available in the left pane are a list of controls that allow you to specify attributes on the mask icon. These options are,
Block frame. The block frame is the rectangle that encloses the block. You can choose
to show or hide the frame by setting the Block Frame
parameter to Visible or
Invisible. The default is to make the block
frame visible. For example, this figure shows visible and invisible block
frames for an AND gate block.

Icon transparency. The icon transparency can be set to Opaque,
Opaque with ports, or
Transparent, based on whether you want to
hide or show what is underneath the icon. The default option
Opaque hides information such as port labels.
The block frame is displayed for a transparent icon, and hidden for the
opaque icon.

For a subsystem block, if you set the icon transparency to
Opaque with ports the port labels are
visible.

Note
For the
Opaqueoption to hide the port labels, there must be an icon drawing command added in the mask editor.If you set the icon transparency to
Transparent, Simulink® does not hide the block frame even if you set the Block Frame property toInvisible.
Icon units. This option controls the coordinate system used by the drawing commands.
It applies only to the plot, text, and
patch drawing commands. You can select from among
these choices: Autoscale,
Normalized, and
Pixel.

Autoscalescales the icon to fit the block frame. When the block is resized, the icon is also resized. For example, this figure shows the icon drawn using these vectors:X = [0 2 3 4 9]; Y = [4 6 3 5 8];

The lower-left corner of the block frame is (0,3) and the upper-right corner is (9,8). The range of the x-axis is 9 (from 0 to 9), while the range of the y-axis is 5 (from 3 to 8).
Normalizeddraws the icon within a block frame whose bottom-left corner is (0,0) and whose top-right corner is (1,1). Only X and Y values from 0 through 1 appear. When the block is resized, the icon is also resized. For example, this figure shows the icon drawn using these vectors:X = [.0 .2 .3 .4 .9]; Y = [.4 .6 .3 .5 .8];

Pixeldraws the icon with X and Y values expressed in pixels. The icon is not automatically resized when the block is resized. To force the icon to resize with the block, define the drawing commands in terms of the block size.
Icon rotation. When the block is rotated or flipped, you can choose whether to rotate or
flip the icon or to have it remain fixed in its original orientation. The
default is not to rotate the icon. The icon rotation is consistent with
block port rotation. This figure shows the results of choosing
Fixed and Rotates
icon rotation when the AND gate block is rotated.

Port rotation. This option enables you to you specify a port rotation type for the masked block. The choices are:
defaultPorts are reordered after a clockwise rotation to maintain a left-to-right port numbering order for ports along the top and bottom of the block and a top-to-bottom port numbering order for ports along the left and right sides of the block.
physicalPorts rotate with the block without being reordered after a clockwise rotation.
The default rotation option is appropriate for control systems and other modeling applications where block diagrams typically have a top-down and left-right orientation. It simplifies editing of diagrams, by minimizing the need to reconnect blocks after rotations to preserve the standard orientation.
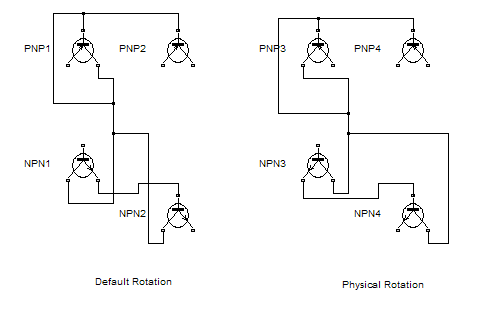
Similarly, the physical rotation option is appropriate for electronic, mechanical, hydraulic, and other modeling applications where blocks represent physical components and lines represent physical connections. The physical rotation option more closely models the behavior of the devices represented (that is, the ports rotate with the block as they would on a physical device). In addition, the option avoids introducing line crossings as the result of rotations, making diagrams easier to read.
For example, the following figure shows two diagrams representing the same transistor circuit. In one, the masked blocks representing transistors use default rotation and in the other, physical rotation.

Both diagrams avoid line crossings that make diagrams harder to read. The next figure shows the diagrams after a single clockwise rotation.
Note
The rotation introduces a line crossing the diagram that uses default rotation but not in the diagram that uses physical rotation. Also that there is no way to edit the diagram with default rotation to remove the line crossing. See Flip or Rotate Blocks for more information.
Run Initialization. The Run initialization option enables you to control the execution of the mask initialization commands. The choices are:
Off (Default): Does not execute the mask initialization commands. When the mask drawing commands do not have dependency on the mask workspace, it is recommended to specify the value of Run initialization as Off. Setting the value to Off helps in optimizing Simulink performance as the mask initialization commands are not executed.
On: Executes the mask initialization commands if the mask workspace is not up-to-date. When this option is specified, the mask initialization commands are executed before executing the mask drawing commands irrespective of the mask workspace dependency of the mask drawing commands.
Analyze: Executes the mask initialization commands only if there is mask workspace dependency. When this option is specified, Simulink executes the mask initialization commands before executing the mask icon drawing commands. The Analyze option is for backward compatibility and is not recommended otherwise. It is recommended that the Simulink models from R2016b or before are upgraded using the Upgrade Advisor.
For more information, see slexMaskDrawingExamples.
Preview
This section displays the preview of block mask icon. Block mask preview is available only if the mask contains an icon drawing.
When you add an icon drawing command and click Apply, the preview image refreshes and is displayed in the Preview section of Icon & Ports pane.
Icon drawing commands
The Icon drawing commands text box available in the center pane enables you to add code to draw the block icon. You can use the list of commands mentioned in the Mask icon drawing commands tables to draw a block icon.
Mask icon drawing commands
| Drawing Command | Description | Syntax Example | Preview |
|---|---|---|---|
color | Change drawing color of subsequent mask icon drawing commands | color('red');
port_label('output',1,'Text') | |
disp | Display text on the masked icon. | disp('Gain') | |
dpoly | Display transfer function on masked icon | dpoly([0 0 1], [1 2 1], 'z') | |
droots | Display transfer function on masked icon | droots([-1], [-2 -3], 4) | |
fprintf | Display variable text centered on masked icon | fprintf('Sum = %d', 7) | |
image | Display RGB image on masked icon Note To add mask icon image from the user interface, click Mask > Add Mask Icon in the context menu.
| image('b747.jpg') | |
patch | Draw color patch of specified shape on masked icon | patch([0 10 20 30 30 0], [10 30 20 25 10 10],[1 0
0]) | |
plot | Draw graph connecting series of points on masked icon | plot([10 20 30 40], [10 20 10 15]) | |
port_label | Draw port label on masked icon | port_label('output', 1, 'xy') | |
text | Display text at specific location on masked icon . You must select |
| |
block_icon | Promote icon of a block contained in a Subsystem to the Subsystem mask | block_icon(BlockName)Here, the icon of block is promoted to its Subsystem block. For more information, see slexblockicon. |
Note
Simulink does not support mask drawing commands within anonymous functions.
The drawing commands execute in the same sequence as they are added in the
Icon drawing commands text box. Drawing commands have
access to all variables in the mask workspace. If any drawing command cannot
successfully execute, the block icon displays question masks ![]() .
.
The drawing commands execute after the block is drawn in these cases:
Changes are made and applied in the mask dialog box.
Changes are made in the Mask Editor.
Changes are done to the block diagram that affects the block appearance, such as rotating the block.
Parameters & Dialog Pane
The Parameters & Dialog pane enables you to design mask dialog boxes using the dialog controls in the Parameters, Display, and Action palettes.

The Parameters & Dialog pane divided into these sections:
Parameter & Dialog Pane
| Section | Section Description | Sub-Section | Sub-Section Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | Controls are elements in a mask dialog box that users can interact with to add or manipulate data. | Parameter | Parameters are user inputs that take part in simulation. The Parameters palette has a set of parameter dialog controls that you can add to a mask dialog box. |
| Display | Controls on the Display palette allow you to group dialog controls in the mask dialog box and display text and images | ||
| Action | Action controls allow you to perform some actions in the mask dialog box. For example, you can click a hyperlink or a button in the mask dialog box. | ||
| Dialog box | You can click or drag and drop dialog controls from the palettes to the Dialog box to create a mask dialog box. | NA | NA |
| Property editor | The Property editor allows you to view and set the properties for the Parameters, Display, and Action controls. | Properties | Defines basic information on all dialog controls, such as Name, Value, Prompt, and Type. |
| Attributes | Defines how a mask dialog control is interpreted. Attributes are related only to parameters. | ||
| Dialog | Defines how dialog controls are displayed in the mask dialog box. | ||
| Layout | Defines how dialog controls are laid out on the mask dialog box. |
Controls
The controls section is sub divided into Parameters, Display, and Action sections. The Controls Table lists the different controls and their description.
Controls Table
| Controls | Description | |
|---|---|---|
Parameters | ||
| Edit | Allows you to enter a parameter value by typing it into the field. You
can associate constraints to an |
| Check box | Accepts a Boolean value. |
| Popup | Allows you to select a parameter value from a list of possible values. When you select the Evaluate check box, the associated variable holds the index of the selected item. Note that the index starts from 1, and not 0. When Evaluate is disabled, the associated variable holds the string of the selected item. |
| Combo box | Allows you to select a parameter value from a list of possible values. You can also type a value either from the list or from outside of the list. When you select the Evaluate check box, the associated variable holds the actual value of the selected item. You can associate constraints to a Combo box parameter. For more information, see the Combo box example in slexMaskParameterOptionsExample. |
| Listbox | Allows you to create a list of parameter values. All options of possible values are displayed on the mask dialog box. You can select multiple values from it. |
| Radio button | Allows you to select a parameter value from a list of possible values. All options for a radio button are displayed on the mask dialog. |
| Slider | Allows you to slide to values within a range defined by minimum and maximum values. A Slider parameter can accept input as a number or a variable name. If the specified variable is a base workspace or a model workspace variable, you can tune the variable value through the Slider. You can tune the values in the linear scale or logarithmic scale using the Scale drop-down menuYou can also control the slider range dynamically. For more information, see slexMaskParameterOptionsExample. Note Values specified for Slider are auto applied.
|
| Dial | Allows you to dial to values within a range defined by minimum and maximum values. A Dial parameter can accept input as a number or a variable name. If the specified variable is a base workspace or a model workspace variable, you can tune the variable value through the Dial. You can tune the values in the linear scale or logarithmic scale using the Scale drop-down menu.You can also control the dial range dynamically. For more information, see slexMaskParameterOptionsExample. Note Values specified for Dial are auto applied.
|
| Spinbox | Allows you to spin through values within a range defined by minimum and maximum values. You can specify a step size for the values. Note Values specified for Spinbox are auto applied.
|
| DataTypeStr | Enables you to specify a data type for a mask parameter. You can associate the Min, Max, and Edit parameters with a data type parameter. For more details, see Specify Data Types Using DataTypeStr Parameter. |
| Min | Specifies a minimum value for the DataTypeStr parameter. |
| Max | Specifies a maximum value for the DataTypeStr parameter. |
| Unit | Allows you to set the measurement units for output or input values of a masked block. The Unit parameter can accept any units of measurement as input. For example, rad/sec for angular velocity, meters/sec2 for acceleration, or distance in km or m. For more information, see slexMaskParameterOptionsExample. |
| Custom Table | Allows you to add tables in the mask dialog box. You can add values as a nested cell array in the Values section of the Property editor. For more information , see slexMaskParameterOptionsExample. |
| Promote parameter | Allows you to selectively promote block parameters from underlying blocks to the mask. Click the Type options field to open the Promoted Parameter Selector dialog box. In this dialog box, you can select the block parameters that you want to promote. Click OK to close it. |
| Promote all | Allows you to promote all underlying block parameters to the mask. When you promote all parameters, the promote operation deletes parameters that have been promoted previously. |
Container | ||
| Panel | Container to group of dialog controls. You use a Panel for logical grouping of dialog controls. |
| Group box | Container to group other dialog controls and containers in the mask dialog box. |
| Tab | Tab to group dialog controls in the mask dialog box. A tab is contained within a tab container. A tab container can have multiple tabs. |
Table | Container to group the Edit, Check box, and the Popup parameters in a tabular form. You can also search and sort the content listed within the Table container. For more information, see the Tables example in Dialog Layout Options and Handling Large Number of Mask Parameters. | |
| CollapsiblePanel | Container to group dialog controls similar to Panel. You can choose to expand or collapse the CollapsiblePanel dialog controls. For more information, see the Collapsible Panel example in Dialog Layout Options. |
Display | ||
| Text | Text displayed in the mask dialog box. |
| Image | Image displayed in the mask dialog box. |
| Text Area | Add a custom text or MATLAB code in the mask dialog box. |
| Listbox Control | Allows you to select a value from a list of possible values. You can select multiple values (Ctrl + click). |
Tree Control | Allows you to select a value from a hierarchical tree of possible values. You can select multiple values (Ctrl + click). | |
Action | ||
| Hyperlink | Hyperlink text displayed on the mask dialog box. |
| Button | Button controls on the mask dialog box. You can program button for specific actions. You can also add an image on a button controls. For more information, see slexMaskParameterOptionsExample. |
Dialog box
You can build a hierarchy of dialog controls by dragging them from a Controls section to the Dialog box. You can also click the palettes on the Controls section to add the required control to the Dialog box. You can add a maximum of 32 levels of hierarchy in the Dialog box.
The Dialog box displays three fields: Type, Prompt, and Name.
The Type field shows the type of the dialog control and cannot be edited. It also displays a sequence number for parameter dialog controls.
The Prompt field shows the prompt text for the dialog control.
The Name field is auto-populated and uniquely identifies the dialog controls. You can choose to add a different value (valid MATLAB name) in the Name field and must not match the built-in parameter name.
The Parameter controls are displayed in light blue background whereas the Display and Action controls are displayed in white background on the Dialog box.
You can move a dialog control in the hierarchy, you can copy and paste a dialog control, you can also delete a node. For more information, see Dialog Control Operations.
Property editor
The Property editor allows you to view and set the properties for Parameter, Display, and Action dialog controls. The Property editor for Parameter is shown:

You can set the following properties for Parameter, Action, and Display dialog controls. For more information, see the Property editor table.
Property editor
| Property | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Properties | |||||||||||||
Name | Uniquely identifies the dialog control in the mask dialog box. The Name property must be set for all dialog controls. | ||||||||||||
Value | Value of the Parameter dialog control. The Value property applies only to the Parameter dialog controls. | ||||||||||||
Prompt | Label text that identifies the parameters in a mask dialog box. The Prompt property applies to all dialog controls except Panel and Image dialog control. | ||||||||||||
Type | Type of the dialog control. You can use the Type field to change the Parameter and Container types. You cannot change any container type to Tab and vice versa. | ||||||||||||
Expand | Allows you to specify if the collapsible panel dialog control is expanded or collapsed, by default. | ||||||||||||
Type options | The Type options property allows you to set specific Parameter properties. The Type options property applies to the Popup, Radio button, DataTypeStr, and Promoted parameters. | ||||||||||||
File path | You can add an image to a mask using the Image dialog control. You can also display an image on a Button dialog control. In either case, provide the path to the image in the File path property that is enabled for these two dialog controls. For the Button dialog control, specify an empty character vector for the Prompt property in order for the image to be displayed. Note that, when you provide the
filepath do not use the quote marks (' '). For example, if
you want to add an image, provide the filepath as :
| ||||||||||||
Word wrap | The Word wrap property enables word wrapping for long text. The Word wrap property applies only for Text dialog control. | ||||||||||||
Maximum and Minimum | The Maximum and Minimum properties enable you to specify a range for controls like Spinbox, Slider, and Dial. | ||||||||||||
Step size | Allows you to specify a step size for the values. This property applies only for Spinbox dialog control. | ||||||||||||
Tooltip | Allows you to specify a tooltip for the selected dialog control type. The tooltip is visible when you hover the cursor over a dialog control on the mask dialog box. You can add tooltips for all dialog controls type except for Group box, Tab, CollapsiblePanel, and Panel. | ||||||||||||
Scale | Allows you to set the tuning scale as
linear or log for
Slider and Dial
dialog controls. | ||||||||||||
| Attributes | |||||||||||||
Evaluate | Simulink uses the value of a mask parameter as you type it in the mask dialog box, or it can evaluate what you specify and use as the result of the evaluation. Select the Evaluate option for a parameter to specify parameter evaluation (the default). To suppress evaluation, clear the option. | ||||||||||||
Tunable | By default, you can change a mask parameter value during simulation. To prevent the changing of parameter value during simulation, clear the Tunable option. If the masked parameter does not support parameter tuning, Simulink ignore the Tunable option setting of a mask parameter. Such parameters are then disabled on the Mask dialog box when simulating. The available modes in Tunable are:
You can also change the mask parameter value while simulating your model on fast restart mode. Depending on the value specified for the Tunable attribute and the simulation mode, the mask parameter can either be read-only or read-write.
For information about parameter tuning and the blocks that support it, see Tune and Experiment with Block Parameter Values. | ||||||||||||
Read only | Indicates that the parameter cannot be modified. | ||||||||||||
Hidden | Indicates that the parameter must not be displayed in the mask dialog box. | ||||||||||||
Never save | Indicates that the parameter value never gets saved in the model file. | ||||||||||||
Constraint | Allows you to add constraints to the selected parameter. | ||||||||||||
| Dialog box | |||||||||||||
Enable | By default Enable is selected. If you clear this option, the selected control becomes unavailable for edit. Masked block users cannot set the value of the parameter. | ||||||||||||
Visible | The selected control appears in the mask dialog box only if this option is selected. | ||||||||||||
Callback | MATLAB code that you want Simulink to execute when a user applies a change to the selected control. Simulink uses a temporary workspace to execute the callback code. | ||||||||||||
| Layout | |||||||||||||
Item location | Allows you to set the location for the dialog control to appear in the current row or a new row. | ||||||||||||
Align Prompts | Allows you to align the parameters on the mask dialog box. This option is supported for all the Display control types except Table. For more information, see Combo box Parameter. | ||||||||||||
Prompt location | Allows you to set the prompt location for the dialog control on either the top or to the left of the dialog control. You cannot set the Prompt location property for Check box, Dial, DataTypeStr, Collapsible Panel and Radiobutton. | ||||||||||||
Orientation | Allows you to specify horizontal or vertical orientation for sliders and radio buttons. | ||||||||||||
Horizontal Stretch | If this option is selected, the controls on the mask dialog box stretch horizontally when you resize the mask dialog box. By default, Horizontal Stretch check box is selected. For more information, see Horizontal Stretch Property. | ||||||||||||
Initialization Pane
The Initialization pane allows you to add MATLAB commands that initialize the masked block.
When you open a model, Simulink locates the visible masked blocks that reside at the top level of the model or in an open subsystem. Simulink only executes the initialization commands for these visible masked blocks if they meet either of the following conditions:
The masked block has icon drawing commands.
Note
Simulink does not initialize masked blocks that do not have icon drawing commands, even if they have initialization commands.
The masked block belongs to a library and has the Allow library block to modify its contents enabled.
Initialization commands for all masked blocks in a model run when you:
Update the diagram
Start simulation
Start code generation
Click Apply on the dialog box
Initialization commands for an individual masked block run when you:
Change any of the mask parameters that define the mask, such as
MaskDisplayandMaskInitialization, by using the Mask Editor or theset_paramcommand.Rotate or flip the masked block, if the icon depends on the initialization commands.
Cause the icon to be drawn or redrawn, and the icon drawing depends on initialization code.
Change the value of a mask parameter by using the block dialog box or the
set_paramcommand.Copy the masked block within the same model or between different models.
The Initialization pane contains the controls described in this section.
Dialog variables
The Dialog variables list displays the names of the dialog controls and associated mask parameters, which are defined in the Parameters & Dialog pane. You can also use the list to change the names of mask parameters. To change a name, double-click the name in the list. An edit field containing the existing name appears. Edit the existing name and click Enter or click outside the edit field to confirm your changes.
Initialization commands
Enter the initialization commands in this field. You can enter any valid MATLAB expression, consisting of MATLAB functions and scripts, operators, and variables defined in the mask workspace. Initialization commands run in the mask workspace, not the base workspace.
Allow library block to modify its contents
This check box is enabled only if the masked block resides in a library. Selecting this option allows you to modify the parameters of the masked block. If the masked block is a masked subsystem, this option allows you to add or delete blocks and set the parameters of the blocks within that subsystem. If this option is not selected, an error is generated when a masked library block tries to modify its contents in any way.
Rules for Initialization commands
Following rules apply for mask initialization commands:
Do not use initialization code to create mask dialogs whose appearance or control settings change depending on changes made to other control settings. Instead, use the mask callbacks provided specifically for this purpose.
Avoid prefacing variable names in initialization commands with
MaskParam_L_andMaskParam_M_. These specific prefixes are reserved for use with internal variable names.Avoid using
set_paramcommands to set parameters of blocks residing in masked subsystems that reside in the masked subsystem being initialized. See Set Up Nested Masked Block Parameters for details.
Documentation Pane
The Documentation pane enables you to define or modify the type, description, and help text for a masked block.

Type
The mask type is a block classification that appears in the mask
dialog box and on all Mask Editor panes for the block. When
Simulink displays a mask dialog box, it suffixes (mask)
to the mask type. To define the mask type, enter it in the
Type field. The text can contain any valid MATLAB character, but cannot contain line breaks.
Description
The mask description is summary help text that describe the block's purpose or function. By default, the mask description is displayed below the mask type in the mask dialog box. To define the mask description, enter it in the Description field. The text can contain any legal MATLAB character. Simulink automatically wraps long lines. You can force line breaks by using the Enter key.
Help
The Online Help for a masked block provides information in addition to that provided by the Type and Description fields. This information appears in a separate window when the masked block user clicks the Help button on the mask dialog box. To define the mask help, type one of these in the Help field:
URL specification
weborevalcommandLiteral or HTML text
Provide a URL. If the first line of the Help field is a URL,
Simulink passes the URL to your default web browser. The URL can begin
with https:, www:,
file:, ftp:, or
mailto:. Examples:
https://www.mathworks.com file:///c:/mydir/helpdoc.html
Once the browser is active, MATLAB and Simulink have no further control over its actions.
Provide a web Command. If the first line of the Help field is a
web command, Simulink passes the command to MATLAB, which displays the specified file in the MATLAB Online Help browser. Example:
web([docroot '/MyBlockDoc/' get_param(gcb,'MaskType') '.html'])
See the MATLAB
web command documentation for
details. A web command used for mask help cannot return
values.
Provide an eval Command. If the first line of the Help field is an
eval command, Simulink passes the command to MATLAB, which performs the specified evaluation. Example:
eval('open My_Spec.doc')See MATLAB
eval command documentation
for details. An eval command used for mask help cannot
return values.
Provide Literal or HTML Text. If the first line of the Help field is not a URL, or
a web or an eval command, Simulink displays the text in the MATLAB Online Help browser under a heading that is the value of the
Mask type field. The text can contain any legal
MATLAB character, line breaks, and any standard HTML tag, including
tags like img that display images.
Simulink first copies the text to a temporary folder, then displays the
text using the web command. If you want the
text to display an image, you can provide a URL path to the image file, or
you can place the image file in the temporary folder. Use tempdir to find the
temporary folder that Simulink uses for your system.
Additional Options
Following buttons appear on the Mask Editor:
The Preview button applies the changes you made, and opens the mask dialog box.
The OK button applies the mask settings and closes the Mask Editor.
The Cancel button closes the Mask Editor without applying any changes you made to the mask.
The Help button displays online information about the Mask Editor.
The Apply button applies the mask settings and leaves the Mask Editor open.
The Unmask button deletes the mask and closes the Mask Editor. To create the mask again, select the block and on the Block tab, in the Mask group, click Create Mask.