How MATLAB Coder Partitions Generated Code
Partitioning Generated Files
By default, during code generation, MATLAB® Coder™ partitions the code to match your MATLAB file structure. This one-to-one mapping lets you easily correlate your files generated in C/C++ with the compiled MATLAB code. MATLAB Coder cannot produce the same one-to-one correspondence for MATLAB functions that are inlined in generated code (see File Partitioning and Inlining).
Alternatively, you can select to generate all C/C++ functions into a single file. For more information, see How to Select the File Partitioning Method. This option facilitates integrating your code with existing embedded software.
How to Select the File Partitioning Method
Using the MATLAB Coder App
To open the Generate dialog box, on the Generate Code page, click the Generate arrow
 .
.Click More Settings.
On the Code Appearance tab, set the Generated file partitioning method to
Generate one file for each MATLAB fileorGenerate all functions into a single file.
At the Command Line
Use the codegen configuration object
FilePartitionMethod option. For example, to compile the
function foo that has no inputs
and generate one C/C++ file for each MATLAB function:
Create a MEX configuration object and set the
FilePartitionMethodoption:mexcfg = coder.config('mex'); mexcfg.FilePartitionMethod = 'MapMFileToCFile';Using the
-configoption, pass the configuration object tocodegen:codegen -config mexcfg -O disable:inline foo % Disable inlining to generate one C/C++ file for each MATLAB function
Partitioning Generated Files with One C/C++ File Per MATLAB File
By default, for MATLAB functions that are not inlined, MATLAB Coder generates one C/C++ file for each MATLAB file. In this case, MATLAB Coder partitions generated C/C++ code so that it corresponds to your MATLAB files.
How MATLAB Coder Partitions Entry-Point MATLAB Functions
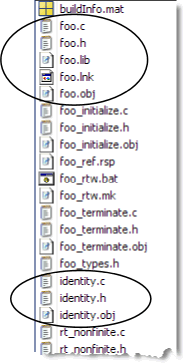
For each entry-point (top-level) MATLAB function, MATLAB Coder generates one C/C++ source, header, and object file with the same name as the MATLAB file.
For example, suppose you define a simple function foo that
calls the function identity. The source file
foo.m contains the following code:
function y = foo(u,v) %#codegen s = single(u); d = double(v); y = double(identity(s)) + identity(d);
Here is the code for identity.m :
function y = identity(u) %#codegen y = u;
In the MATLAB
Coder app, to generate a C static library for foo.m:
Define the inputs
uandv. For more information, see Specify Properties of Entry-Point Function Inputs Using the App.To open the Generate dialog box, on the Generate Code page, click the Generate arrow
 .
.Set the Build type to
Static LibraryClick More Settings.
On the All Settings tab, under Function Inlining, set the Inline threshold parameter to
0Click Close
To generate the library, click Generate.
To generate a C static library for foo.m, at the command line,
enter:
codegen -config:lib -O disable:inline foo -args {0, 0}
% Use the -args option to specify that u and v are both
% real, scalar doublesMATLAB
Coder generates source, header, and object files for foo
and identity in your output folder.
How MATLAB Coder Partitions Local Functions
For each local function, MATLAB
Coder generates code in the same C/C++ file as the calling function. For
example, suppose you define a function foo that calls a local
function
identity:
function y = foo(u,v) %#codegen s = single(u); d = double(v); y = double(identity(s)) + identity(d); function y = identity(u) y = u;
To generate a C++ library, before generating code, select a C++ compiler and set C++ as your target language. For example, at the command line:
Select C++ as your target language:
cfg = coder.config('lib') cfg.TargetLang='C++'Generate the C++ library:
codegen -config cfg foo -args {0, 0} % Use the -args option to specify that u and v are both % real, scalar doublesIn the primary function
foo, MATLAB Coder inlines the code for theidentitylocal function.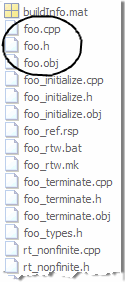
Note
If you specify
C++, MATLAB Coder wraps theCcode into.cppfiles so that you can use aC++compiler and interface with externalC++applications. It does not generateC++classes.Here is an excerpt of the generated code in
foo.cpp:... /* Function Definitions */ double foo(double u, double v) { return (double)(float)u + v; } ...
How MATLAB Coder Partitions Overloaded Functions
An overloaded function is a function that has multiple implementations to accommodate different classes of input. For each implementation (that is not inlined), MATLAB Coder generates a separate C/C++ file with a unique numeric suffix.
For example, suppose you define a simple function
multiply_defined:
%#codegen function y = multiply_defined(u) y = u+1;
You then add two more implementations of multiply_defined, one
to handle inputs of type single (in an @single
subfolder) and another for inputs of type double (in an
@double subfolder).
To call each implementation, define the function
call_multiply_defined:
%#codegen function [y1,y2,y3] = call_multiply_defined y1 = multiply_defined(int32(2)); y2 = multiply_defined(2); y3 = multiply_defined(single(2));
Next, generate C code for the overloaded function
multiply_defined. For example, at the MATLAB command line,
enter:
codegen -O disable:inline -config:lib call_multiply_defined
MATLAB
Coder generates C source, header, and object files for each implementation of
multiply_defined, as highlighted. Use numeric suffixes to
create unique file names.

Generated Files and Locations
The types and locations of generated files depend on the target that you specify. For all targets, if errors or warnings occur during build or if you explicitly request a report, MATLAB Coder generates reports.
Each time MATLAB Coder generates the same type of output for the same code or project, it removes the files from the previous build. If you want to preserve files from a build, copy them to a different location before starting another build.
Generated Files for MEX Targets
By default, MATLAB
Coder generates the following files for MEX function (mex)
targets.
| Type of Files | Location |
|---|---|
| Platform-specific MEX files | Current folder |
MEX, and C/C++ source, header, and object files | codegen/mex/function_name |
HTML reports | codegen/mex/function_name/html |
Generated Files for C/C++ Static Library Targets
By default, MATLAB Coder generates the following files for C/C++ static library targets.
| Type of Files | Location |
|---|---|
C/C++ source, library, header, and object files | codegen/lib/function_name |
HTML reports | codegen/lib/function_name/html |
Generated Files for C/C++ Dynamic Library Targets
By default, MATLAB Coder generates the following files for C/C++ dynamic library targets.
| Type of Files | Location |
|---|---|
C/C++ source, library, header, and object files | codegen/dll/function_name |
HTML reports | codegen/dll/function_name/html |
Generated Files for C/C++ Executable Targets
By default, MATLAB Coder generates the following files for C/C++ executable targets.
| Type of Files | Location |
|---|---|
C/C++ source, header, and object files | codegen/exe/function_name |
HTML reports | codegen/exe/function_name/html |
Changing Names and Locations of Generated Files
Using the MATLAB Coder App
| To change | Action |
|---|---|
| The output file name |
|
| The output file location |
|
At the Command Line. You can change the name and location of generated files by using the codegen options
-o and -d.
File Partitioning and Inlining
How MATLAB Coder partitions generated C/C++ code depends on whether you choose to generate one C/C++ file for each MATLAB file and whether you inline your MATLAB functions.
| If you | MATLAB Coder |
|---|---|
| Generate all C/C++ functions into a single file and disable inlining | Generates a single C/C++ file without inlining functions. |
| Generate all C/C++ functions into a single file and enable inlining | Generates a single C/C++ file. Inlines functions whose sizes fall within the inlining threshold. |
| Generate one C/C++ file for each MATLAB file and disable inlining | Partitions generated C/C++ code to match MATLAB file structure. See Partitioning Generated Files with One C/C++ File Per MATLAB File. |
| Generate one C/C++ file for each MATLAB file and enable inlining | Places inlined functions in the same C/C++ file as the function into which they are inlined. Even when you enable inlining, MATLAB Coder inlines only those functions whose sizes fall within the inlining threshold. For MATLAB functions that are not inlined, MATLAB Coder partitions the generated C/C++ code, as described. |
Tradeoffs Between File Partitioning and Inlining
Weighing file partitioning against inlining represents a trade-off between readability, efficiency, and ease of integrating your MATLAB code with existing embedded software.
| If You Generate | Generated C/C++ Code | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| All C/C++ functions into a single file | Does not match MATLAB file structure | Easier to integrate with existing embedded software | Difficult to map C/C++ code to original MATLAB file |
| One C/C++-file for each MATLAB file and enable inlining | Does not exactly match MATLAB file structure | Program executes faster | Difficult to map C/C++ code to original MATLAB file |
| One C/C++-file for each MATLAB file and disable inlining | Matches MATLAB file structure | Easy to map C/C++ code to original MATLAB file | Program runs less efficiently |
How Disabling Inlining Affects File Partitioning
Inlining is enabled by default. Therefore, to generate one C/C++ file for each top-level MATLAB function, you must:
Select to generate one C/C++ file for each top-level MATLAB function. For more information, see How to Select the File Partitioning Method.
Explicitly disable inlining, either globally or for individual MATLAB functions.
How to Disable Inlining Globally Using the MATLAB Coder App
To open the Generate dialog box, on the Generate Code page, click the Generate arrow
 .
.Click More Settings.
On the All Settings tab, under Function Inlining set the Inline threshold to
0.
How to Disable Inlining Globally at the Command Line. To disable inlining of functions, use the -O disable:inline
option with codegen. For example, to disable inlining and
generate a MEX function for a function foo that has
no inputs:
codegen -O disable:inline foo
For more information, see the description of codegen.
How to Disable Inlining for Individual Functions. To disable inlining for an individual MATLAB function, add the directive
coder.inline('never'); on a
separate line in the source MATLAB file, after the function
signature.
function y = foo(u,v) %#codegen coder.inline('never'); s = single(u); d = double(v); y = double(identity(s)) + identity(d);
codegen does not inline entry-point functions.
The coder.inline directive applies only
to the function in which it appears. In this example, inlining is disabled for
function foo, but not for identity, a
top-level function defined in a separate MATLAB file and called by foo. To disable inlining for
identity, add this directive after its function signature in
the source file identity.m. For more information, see
coder.inline.
For a more efficient way to disable inlining for both functions, see How to Disable Inlining Globally at the Command Line.
Correlating C/C++ Code with Inlined Functions
To correlate the C/C++ code that you generate with the original inlined functions, add comments in the MATLAB code to identify the function. These comments will appear in the C/C++ code and help you map the generated code back to the original MATLAB functions.
Modifying the Inlining Threshold
To change inlining behavior, adjust the inlining threshold parameter.
Modifying the Inlining Threshold Using the MATLAB Coder App
To open the Generate dialog box, on the Generate Code page, click the Generate arrow
 .
.Click More Settings.
On the All Settings tab, under Function Inlining, set the value of the Inline threshold parameter.
Modifying the Inlining Threshold at the Command Line. Set the value of the InlineThreshold parameter of the
configuration object. See coder.MexCodeConfig, coder.CodeConfig, coder.EmbeddedCodeConfig.