hankelsv
Compute Hankel singular values for stable/unstable or continuous/discrete system
Syntax
hankelsv(G) hankelsv(G,ErrorType,style) [sv_stab,sv_unstab]=hankelsv(G,ErrorType,style)
Description
[sv_stab,sv_unstab]=hankelsv(G,ErrorType,style) returns a column vector SV_STAB containing the Hankel singular values of the stable part of G and SV_UNSTAB of anti-stable part (if it exists). The Hankel SV's of anti-stable part ss(a,b,c,d) is computed internally via ss(-a,-b,c,d). Discrete model is converted to continuous one via the bilinear transform.
hankelsv(G) with no output arguments draws a bar graph of the Hankel singular values such as the following:
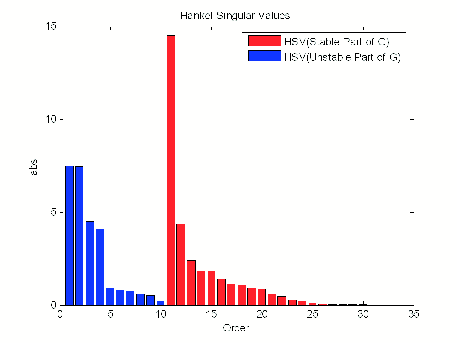
This table describes optional input arguments for hankelsvd.
Argument | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
ERRORTYPE |
| Regular Hankel SV's of G Hankel SV's of phase matrix Hankel SV's of coprime factors |
STYLE |
| Absolute value logarithm scale |
Algorithms
IfErrorType = 'add', then hankelsv implements the numerically robust square root method to compute the Hankel singular values [1]. Its algorithm goes as follows:
Given a stable model G, with controllability and observability grammians P and Q, compute the SVD of P and Q:
[Up,Sp,Vp] = svd(P); [Uq,Sq,Vq] = svd(Q);
Then form the square roots of the grammians:
Lr = Up*diag(sqrt(diag(Sp))); Lo = Uq*diag(sqrt(diag(Sq)));
The Hankel singular values are simply:
σH =svd(Lo'*Lr);
This method not only takes the advantages of robust SVD algorithm, but also ensure the computations stay well within the “square root” of the machine accuracy.
If ErrorType = 'mult', then hankelsv computes the Hankel singular value of the phase matrix of G [2].
If ErrorType = 'ncf', then hankelsv computes the Hankel singular value of the normalized coprime factor pair of the model [3].
References
[1] Safonov, M.G., and R.Y. Chiang, “A Schur Method for Balanced Model Reduction,” IEEE Trans. on Automat. Contr., vol. AC-2, no. 7, July 1989, pp. 729-733.
[2] Safonov, M.G., and R.Y. Chiang, “Model Reduction for Robust Control: A Schur Relative Error Method,” International J. of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, Vol. 2, pp. 259-272, 1988.
[3] Vidyasagar, M., Control System Synthesis - A Factorization Approach. London: The MIT Press, 1985.