Copy and Paste Stateflow Objects
The Clipboard object is an interface to the clipboard used for
copying and pasting Stateflow® objects. Unlike other Stateflow API objects, there is only one Clipboard object. You
can use the Clipboard object to copy and paste graphical and
nongraphical objects within the same chart, between charts in the same Simulink® model, or between charts in different Simulink models.
Access the Clipboard Object
Create a handle to the Clipboard object by calling the
sfclipboard function.
cb = sfclipboard;
The Clipboard object has two methods used to copy and paste
objects from one location to another.
Copying Objects to the Clipboard
The copy method copies the
specified objects to the Clipboard object.
cb.copy(objects);
You cannot copy a mixture of graphical and nongraphical objects to the clipboard in the same operation. Instead, the objects you copy must be all graphical (states, boxes, functions, transitions, junctions, and annotations) or all nongraphical (data, events, and messages).
Copying graphical objects also copies the data, event, and message objects that the graphical objects contain.
All graphical objects copied in a single copy operation must be visible in the same subviewer. In other words, to copy graphical objects in a single operation, they must reside in the same chart or subchart.
To maintain the transition connections and containment relationships between copied objects, you must:
Copy a grouped state to the clipboard. By copying a grouped state, you copy all the objects contained in the state, as well as all the relationships among these objects by using a single operation.
Copy an array of related objects. For example, to copy two states connected by a transition to another container, first create an array that contains both the states and the transition. Then you can copy the array to the clipboard.
Pasting Objects from the Clipboard
The pasteTo method pastes the
contents of the clipboard to a new container.
cb.pasteTo(container)
If the clipboard contains graphical objects (states, boxes, functions,
transitions, junctions, and annotations), the container must be a chart or a
subchart. To convert a state, box, or graphical function to a subchart, set its
IsSubchart property to true. After
pasting, you can convert the container back by setting its
IsSubchart property to false.
Copy by Grouping
When you copy and paste a grouped state, you copy not only the state but all of its contents. This method is the simplest way of copying objects by using the Stateflow API.
For the example, suppose that ch is a handle to this
chart.
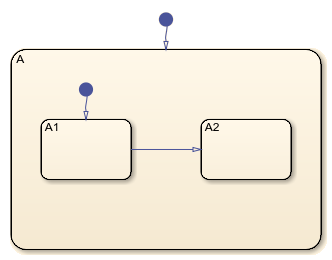
You can make a copy of state A and its contents by setting the
value of the property IsGrouped to true before
copying and pasting the state.
Find a handle to state
A.sA = ch.find('-isa','Stateflow.State','Name','A');
Group the state and its contents by setting the
IsGroupedproperty for the state totrue. Save the previous setting of this property so you can revert to it later.prevGrouping = sA.IsGrouped; sA.IsGrouped = true;
Change the name of the state to
'Copy_of_A'. Save the previous name so you can revert to it later.prevName = sA.Name; newName = ['Copy_of_' prevName]; sA.Name = newName;Create a handle to the clipboard object.
cb = sfclipboard;
Copy the grouped state to the clipboard.
cb.copy(sA);
Restore the state properties to their original settings.
sA.IsGrouped = prevGrouping; sA.Name = prevName;
Paste a copy of the objects from the clipboard to the chart.
cb.pasteTo(ch);
Adjust the state properties of the new state.
sNew = ch.find('-isa','Stateflow.State','Name',newName); sNew.Position = sA.Position + [400 0 0 0]; sNew.IsGrouped = prevGrouping;

Copy Objects Individually
You can also copy individual objects from one location to another. However, in order to preserve transition connections and containment relationships between objects, you must copy all the connected objects at once. Before copying to the clipboard, create an array of objects by appending the results of successive searches.
For the example, suppose that ch is a handle to this
chart.

You can copy states A1 and A2, along with
the transition between them, to a new state.
Find a handle to state
A.sA = ch.find('-isa','Stateflow.State','Name','A');
Add a new state called
B. To enable pasting other objects insideB, convert the new state to a subchart.sB = Stateflow.State(ch); sB.Name = 'B'; sB.Position = sA.Position + [400 0 0 0]; sB.IsSubchart = true;Create an array called
sourceObjsthat contains handles to the states and transitions in stateA. Use the functionsetdiffto remove stateAfrom the array of objects to copy.objArrayS = sA.find('-isa','Stateflow.State'); objArrayS = setdiff(objArrayS,sA); objArrayT = sA.find('-isa','Stateflow.Transition'); sourceObjs = [objArrayS ; objArrayT];
Create a handle to the clipboard object.
cb = sfclipboard;
Copy the objects in
sourceObjsand paste them inB.cb.copy(sourceObjs); cb.pasteTo(sB);
Convert
Bback to a state.sB.IsSubchart = false; sB.IsGrouped = false;
Reposition the states and transitions in
B.newStates = sB.find('-isa','Stateflow.State'); newStates = setdiff(newStates,sB); newTransitions = sB.find('-isa','Stateflow.Transition'); newOClocks = get(newTransitions,{'SourceOClock','DestinationOclock'}); newPositions = get(newStates,'Position'); for i = 1:numel(newPositions) set(newStates(i),'Position',newPositions{i} + [25 35 0 0]); end set(newTransitions,{'SourceOClock','DestinationOclock'},newOClocks);

You can also copy nongraphical data, event, and message objects individually. However, since there is no way for these objects to find their new parents, you must ensure that you copy each of these objects separately to its appropriate parent object.
See Also
find | pasteTo | setdiff | sfclipboard | Stateflow.State