Processor and FPGA Synchronization
In the HDL Workflow Advisor, you can choose a Processor/FPGA synchronization mode for your processor and FPGA when you:
Generate a custom IP core to use in an embedded system integration project.
Use the Simulink Real-Time FPGA I/O workflow.
The following synchronization modes are available:
Free running(default)Coprocessing – blockingCoprocessing – nonblocking with delay(available only for the Simulink Real-Time FPGA I/O workflow)
Free Running Mode
In free running mode, the processor and FPGA each run nonsynchronized, continuously, and in parallel.
Select Free running as the Processor/FPGA synchronization mode when you do not want your processor and FPGA to be automatically synchronized.
The following diagram shows how the processor and FPGA can communicate in free running mode. The shaded areas indicate that the processor and FPGA are running continuously.

Coprocessing – Blocking Mode
In blocking coprocessor mode, HDL Coder™ automatically generates synchronization logic for the FPGA so that the processor and FPGA run in tandem.
Select Coprocessing – blocking as the Processor/FPGA synchronization mode when FPGA execution time is short relative to the processor sample time, and you want the FPGA to complete before the processor continues.
The following diagram shows how the processor and FPGA run in blocking coprocessing mode.
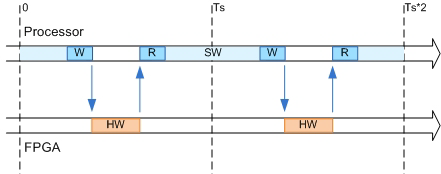
The shaded areas indicate when the processor and FPGA are running. During each sample time, the processor writes to the FPGA, then stops and waits for an indication that the FPGA has finished processing before continuing to run. Each time the FPGA runs, it executes the logic generated for one DUT subsystem sample time.
Coprocessing – Nonblocking With Delay Mode
In delayed nonblocking coprocessor mode, HDL Coder automatically generates synchronization logic for the FPGA so that the processor and FPGA run in tandem. This mode is only available to Speedgoat IO modules that use Xilinx® ISE with the Simulink Real-Time FPGA I/O workflow.
Select Coprocessing – nonblocking with delay as the Processor/FPGA synchronization mode when the FPGA processing time is long relative to the processor sample time, or you do not want the processor to wait for the FPGA to finish before the processor continues to run.
The following diagram shows how the processor and FPGA run in delayed nonblocking coprocessor mode.
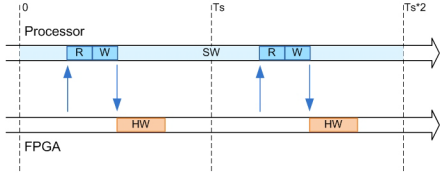
The shaded areas indicate when the processor and FPGA are running. During each sample time, the processor reads FPGA data from the previous sample time, then writes to the FPGA and continues to run without waiting for the FPGA to finish. Each time the FPGA runs, it executes the logic generated for one DUT subsystem sample time.