Visualize and Investigate Sequence Read Alignments
When to Use the NGS Browser to Visualize and Investigate Data
The NGS Browser lets you visually verify and investigate the alignment of sequence reads to a reference sequence, in support of analyses that measure genetic variations and gene expression. The NGS Browser lets you:
Visualize sequence reads aligned to a nucleotide reference sequence.
Compare multiple data sets aligned against a common reference sequence.
View coverage of different bases and regions of the reference sequence.
Investigate quality and other details of aligned reads.
Identify mismatches due to base-calling errors or polymorphisms.
Visualize insertions and deletions.
Retrieve feature annotations relative to a specific region of the reference sequence.
Investigate regions of interest in the alignment, determined by various analyses.
You can visualize and investigate the aligned data before, during, or after any preprocessing (filtering, quality recalibration) or analysis steps you perform on the aligned data.
Open the NGS Browser
To open the NGS Browser, type the following in the MATLAB Command Window:
ngsbrowser
Alternatively, click the NGS Browser on the Apps tab.

Import Data into the NGS Browser
Browser Displaying Reference Track, One Alignment Track, and One Annotation Track

Import a Reference Sequence
You can import a single reference sequence into the NGS Browser. The reference sequence must be in a FASTA file.
Select File > Add Data from File.
In the Open dialog box, select a FASTA file, and then click Open.
Tip
You can use the getgenbank function with the
ToFile and SequenceOnly name-value pair
arguments to retrieve a reference sequence from the GenBank database and save it to a FASTA-formatted file.
Import Sequence Read Alignment Data
You can import multiple data sets of sequence read alignment data. The alignment data must be in either of the following:
BioMapobjectTip
Construct a BioMap object from a SAM- or BAM-formatted file to investigate, subset, and filter the data before importing it into the NGS Browser.
SAM- or BAM-formatted file
Note
Your SAM- or BAM-formatted file must:
Have reads ordered by start position in the reference sequence.
Have an IDX index file (for a SAM-formatted file) or BAI and LINEARINDEX index files (for a BAM-formatted file) stored in the same location as your source file. Otherwise, the source file must be stored in a location to which you have write access, because MATLAB® needs to create and store index files in this location.
Tip
Try using SAMtools to check if the reads in your SAM- or BAM-formatted file are ordered by position in the reference sequence, and also to reorder them, if needed.
Tip
If you do not have index files (IDX or BAI and LINEARINDEX) stored in the same location as your source file, and your source file is stored in a location to which you do not have write access, you cannot import data from the source file directly into the browser. Instead, construct a
BioMapobject from the source file using theIndexDirname-value pair argument, and then import the BioMap object into the browser.
To import sequence read alignment data:
Select File > Add Data from File or File > Import Alignment Data from MATLAB Workspace.
Select a SAM-formatted file, BAM-formatted file, or BioMap object.
If you select a file containing multiple reference sequences, in the Select Reference dialog box, select a reference or scan the file for available references and their mapped reads counts. Click OK.
Repeat the previous steps to import additional data sets.
Import Feature Annotations
You can import multiple sets of feature annotations from GFF- or GTF-formatted files that contain data for a single reference sequence.
Select File > Add Data from File.
In the Open dialog box, select a GFF- or GTF-formatted file, and then click Open.
Repeat the previous steps to import additional annotations.
Zoom and Pan to a Specific Region of the Alignment
To zoom in and out:
| Use the |
| or click-drag an edge of the rubberband in the Overview area. |
|
|
To pan across the alignment:
| Use the |
| or click-drag the rubberband in the Overview area. |
|
|
Tip
Use the left and right arrow keys to pan in one base pair (bp) increments.
View Coverage of the Reference Sequence
At the top of each alignment track, the coverage view displays the coverage of each base in the reference sequence. The vertical ruler on the left edge of the coverage view indicates the maximum coverage in the display range. Hover the mouse pointer over a position in the coverage view to display the location and counts.
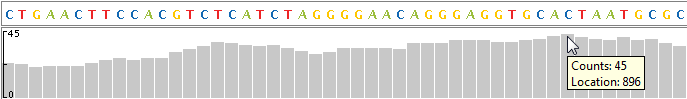
Note
The browser computes coverage at the base pair resolution, instead of binning, even when zoomed out.
To change the percent coverage displayed, click anywhere in the alignment track, and then edit the Alignment Coverage settings.

Tip
Set Max to a value greater than 100, if needed, when comparing the coverage of multiple tracks of reads.
View the Pileup View of Short Reads
Each alignment track includes a pileup view of the short reads aligned to the reference sequence.

Limit the depth of the reads displayed in the pileup view by setting the Maximum display read depth in the Alignment Pileup settings.

Tip
Limiting the depth of short reads in the pileup view does not change the counts displayed in the coverage view.
Compare Alignments of Multiple Data Sets
Compare multiple data sets, with each data set in its own track, against a common reference sequence. Use the Track List to show/hide, order, and delete tracks of data.

View Location, Quality Scores, and Mapping Information
Hover the mouse pointer over a position in a read to display strand direction, location, quality, and mapping information for the base, the read, and its paired mate.

Flag Reads
Click anywhere in an alignment track to display the Alignment Pileup settings.

Flag Reads with Low Mapping Quality
Set the Mapping quality threshold in the Alignment Pileup section to flag low-quality reads. Reads with a mapping quality below this level appear in a lighter shade of gray.
Flag Duplicate Reads
Select Flag duplicate reads and select an outline color.
Flag Reads with Unmapped Pairs
Select Flag reads with unmapped pair and select an outline color.
Evaluate and Flag Mismatches
Mismatches display as colored blocks or letters, depending on the zoom level.
Zoomed out view of read — Mismatches display as bars
![]()
Zoomed in view of read — Mismatches display as letters
![]()
In addition to the base Phred quality information that displays in the tooltip, you can visualize quality differences by using the Shade mismatch bases by Phred quality settings.

The mismatch blocks or letters display in:
Light shade — Mismatch bases with Phred scores below the minimum
Graduation of medium shades — Mismatch bases with Phred scores within the minimum to maximum range
Dark shade — Mismatch bases with Phred scores above the maximum
View Insertions and Deletions
The NGS Browser designates insertions with a ![]() symbol. Hover the mouse pointer over the insertion symbol
to display information about it.
symbol. Hover the mouse pointer over the insertion symbol
to display information about it.

The NGS Browser designates deletions with dashes.

View Feature Annotations
After importing a feature annotation file, you can zoom and pan to view feature annotations associated with a region of interest in the alignment. Hover the mouse pointer over the feature annotation.

Print and Export the Browser Image
Print or export the browser image by selecting File > Print Image or File > Export Image.