Table Array Data Types in App Designer Apps
Table arrays are useful for storing tabular data as MATLAB® variables. For example, you can call the readtable function to
create a table array from a spreadsheet.
Table UI components, by contrast, are user interface
components that display tabular data in apps. Starting in R2018a, the types
of data you can display in a Table UI component include
table arrays. Only App Designer apps and figures created with the uifigure function
support table arrays.
When you display table array data in apps, you can take advantage of the
interactive features for certain data types. And unlike other types of
arrays that Table UI components support, table array data
does not display according to the ColumnFormat property
of the Table UI component.
Logical Data
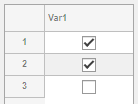
In a Table UI component, logical values display as
check boxes. true values are checked, whereas
false values are unchecked. When the
ColumnEditable property of the
Table UI component is
true, the user can select and clear the
check boxes in the app.
fig = uifigure; tdata = table([true; true; false]); uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata); uit.Position(3) = 130; uit.RowName = 'numbered';
Categorical Data
categorical values can appear as drop-down lists or
as text. The categories appear in drop-down lists when the
ColumnEditable property of the
Table UI component is
true. Otherwise, the categories display
as text without a drop-down list.
fig = uifigure;
cnames = categorical({'Blue';'Red'},{'Blue','Red'});
w = [400; 700];
tdata = table(cnames,w,'VariableNames',{'Color','Wavelength'});
uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata,'ColumnEditable',true);

If the categorical array is not protected, users
can add new categories in the running app by typing in the
cell.
Datetime Data
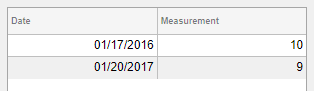
datetime values display according to the
Format property of the corresponding
table variable (a datetime array).
fig = uifigure; dates = datetime([2016,01,17; 2017,01,20],'Format','MM/dd/uuuu'); m = [10; 9]; tdata = table(dates,m,'VariableNames',{'Date','Measurement'}); uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata);
To change the format, use dot notation to set the
Format property of the table variable.
Then, replace the data in the Table UI component.
tdata.Date.Format = 'dd/MM/uuuu';
uit.Data = tdata;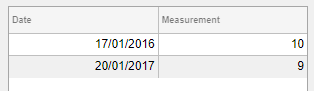
When the ColumnEditable property of the
Table UI component is
true, users can change date values in the
app. When the column is editable, the app expects input values that
conform to the Format property of the
datetime array. If the user enters an
invalid date, the value displayed in the table is
NaT.
Duration Data
duration values display according to the
Format property of the corresponding
table variable (a duration array).
fig = uifigure; mtime = duration([0;0],[1;1],[20;30]); dist = [10.51; 10.92]; tdata = table(mtime,dist,'VariableNames',{'Time','Distance'}); uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata);

To change the format, use dot notation to set the
Format property of the table variable.
tdata.Time.Format = 's';
uit.Data = tdata;
Cells containing duration values are not editable
in the running app, even when ColumnEditable of
the Table UI component is
true.
Nonscalar Data
Nonscalar values display in the app the same way as they display in
the Command Window. For example, this table array contains 3-D
arrays and struct arrays.
fig = uifigure;
arr = {rand(3,3,3); rand(3,3,3)};
s = {struct; struct};
tdata = table(arr,s,'VariableNames',{'Array','Structure'});
uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata);
A multicolumn table array variable displays as a combined column in
the app, just as it does in the Command Window. For example, the
RGB variable in this table array is a
3-by-3
array.
n = [1;2;3]; rgbs = [128 122 16; 0 66 155; 255 0 0]; tdata = table(n,rgbs,'VariableNames',{'ROI','RGB'})
tdata =
3×2 table
ROI RGB
___ _________________
1 128 122 16
2 0 66 155
3 255 0 0The Table UI component provides a similar
presentation. Selecting an item in the RGB column
selects all the subcolumns in that row. The values in the subcolumns
are not editable in the running app, even when
ColumnEditable property of the
Table UI component is
true.
fig = uifigure;
uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata);
Missing Data Values
Missing values display as indicators according to the data type:
Missing strings display as
<missing>.Undefined
categoricalvalues display as<undefined>.Invalid or undefined numbers or
durationvalues display asNaN.Invalid or undefined
datetimevalues display asNaT.
If the ColumnEditable property
of the Table UI component is
true, then the user can correct the
values in the running app.
fig = uifigure;
sz = categorical([1; 3; 4; 2],1:3,{'Large','Medium','Small'});
num = [NaN; 10; 12; 15];
tdata = table(sz,num,'VariableNames',{'Size','Number'});
uit = uitable(fig,'Data',tdata,'ColumnEditable',true);
Example: App that Displays a Table Array
This app shows how to display a Table UI component in an app that uses table array data. The table array contains numeric, logical, categorical, and multicolumn variables.
The StartupFcn callback loads a spreadsheet into a table array. Then a subset of the data displays and is plotted in the app. One plot displays the original table data. The other plot initially shows the same table data, and then updates when the user edits a value or sorts a column in the Table UI component.
