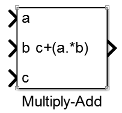
Multiply-Add
Multiply-add combined operation
Library
HDL Coder / HDL Operations
Description
The Multiply-Add block computes the product of the first two inputs, a and b, and adds the result to the third input, c. The inputs can be vectors or scalars.
The multiplication operation is full precision, regardless of the output type. The Integer rounding mode, Output data type, and Saturate on integer overflow settings apply only to the addition operation.
Use the Multiply-Add block to map a combined multiply-add or a multiply-subtract operation to a DSP unit in your target hardware. You can select the Function setting in the Block Parameters dialog box for the Multiply-Add block.
To map to a DSP unit, specify the SynthesisTool property for your
model. When you generate HDL code for your model, HDL Coder™ configures the multiply-add operation so that your synthesis tool can map
to a DSP unit.
Note
Some DSP units do not have the multiply-add capability. To see if your hardware has the multiply-add capability, refer to the documentation for the hardware.
Data Type Support
The Multiply-Add block accepts and outputs signals of numeric data type that Simulink® supports, including fixed-point data types.
You can use matrix data types with the Multiply-Add block. When you use
these types, the port dimensions of the inputs a and
b must match. For example, in MATLAB®, you can perform these matrix
operations:
a = [1 2; 3 4]; b = [5; 6]; c = 7; c + (a.*b)
ans =
12 17
25 31
Error in port widths or
dimensions.Parameters
Function
Specify the function to perform a combined multiply and add or a multiply and subtract operation.
Default:
c+(a.*b)
You can set the function to:
c+(a.*b)c-(a.*b)(a.*b)-c
Output data type
Specify the output data type.
Default:
Inherit: Inherit via internal rule
Set the output data type to:
A rule that inherits a data type, for example,
Inherit: Same as inputAn expression that evaluates to a valid data type, for example,
fixdt([],16,0)
Click the Show data type assistant button
![]() to display the Data Type Assistant dialog
box, which helps you to set the Output data type
parameter.
to display the Data Type Assistant dialog
box, which helps you to set the Output data type
parameter.
For more information, see Control Signal Data Types .
Integer rounding mode
Specify the rounding mode for fixed-point operations.
Default:
Floor
CeilingRounds positive and negative numbers toward positive infinity. Equivalent to the MATLAB
ceilfunction.ConvergentRounds number to the nearest representable value. If a tie occurs, rounds to the nearest even integer. Equivalent to the Fixed-Point Designer™
convergentfunction.FloorRounds positive and negative numbers toward negative infinity. Equivalent to the MATLAB
floorfunction.NearestRounds number to the nearest representable value. If a tie occurs, rounds toward positive infinity. Equivalent to the Fixed-Point Designer
nearestfunction.RoundRounds number to the nearest representable value. If a tie occurs, rounds positive numbers toward positive infinity and rounds negative numbers toward negative infinity. Equivalent to the Fixed-Point Designer
roundfunction.SimplestChooses between rounding toward floor and rounding toward zero to generate rounding code that is as efficient as possible.
ZeroRounds number toward zero. Equivalent to the MATLAB
fixfunction.
See Block-Specific Parameters for the command-line information.
For more information, see Rounding.
Saturate on integer overflow
Specify whether overflows saturate.
Default: Off
 On
OnOverflows saturate to either the minimum or maximum value that the data type can represent.
For example, an overflow associated with a signed 8-bit integer can saturate to -128 or 127.
 Off
OffOverflows wrap to the appropriate value that the data type can represent.
For example, the number 130 does not fit in a signed 8-bit integer and wraps to -126.
Consider selecting this check box when your model has a possible overflow and you want explicit saturation protection in the generated code.
Consider clearing this check box when you want to optimize efficiency of your generated code.
Clearing this check box also helps you to avoid overspecifying how a block handles out-of-range signals. For more information, see Troubleshoot Signal Range Errors.
When you select this check box, saturation applies to every internal operation on the block, not just the output or result.
In general, the code generation process can detect when overflow is not possible. In this case, the code generator does not produce saturation code.
Parameter:
SaturateOnIntegerOverflow |
| Type: character vector |
Value:
'off' | 'on' |
Default:
'off' |