
| Signal Processing Toolbox | Help Desk |
interp
Increase sampling rate by an integer factor (interpolation).
y = interp(x,r) y = interp(x,r,l,alpha) [y,b] = interp(x,r,l,alpha)Interpolation increases the original sampling rate for a sequence to a higher rate.
interp performs lowpass interpolation by inserting zeros into the original sequence and then applying a special lowpass filter.
y = interp(x,r)
increases the sampling rate of x by a factor of r. The interpolated vector y is r times longer than the original input x.
y = interp(x,r,l,alpha)
specifies l (filter length) and alpha (cut-off frequency). The default value for l is 4 and the default value for alpha is 0.5.
[y,b] = interp(x,r,l,alpha)
returns vector b containing the filter coefficients used for the interpolation.
Interpolate a signal by a factor of four:
t = 0:0.001:1; % time vector x = sin(2*pi*30*t) + sin(2*pi*60*t); y = interp(x,4); stem(x(1:30)) stem(y(1:120)), axis([0 120 -2 2])

interp uses the lowpass interpolation Algorithm 8.1 described in [1]:
l*r+1. The number of original sample values used for interpolation is 2*l. Ordinarily, l should be less than or equal to 10. The original signal is assumed to be band limited with normalized cutoff frequency 0 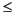
alpha 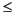
1, where 1 is half the original sampling frequency (the Nyquist frequency). The default value for l is 4 and the default value for alpha is 0.5.
If r is not an integer, interp gives the following error message:
Resampling rate R must be an integer.
1-D data interpolation (table lookup) (see MATLAB Function Reference). |
|